Samsung 1999 Annual Report Download - page 50
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 50 of the 1999 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
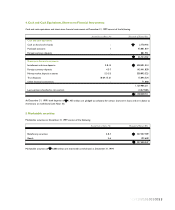
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Short-term Financial Instruments -
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and in bank
accounts, with original maturities of three months or less.
Investments which are readily convertible into cash within four
to twelve months of purchase are classified in the balance
sheet as short-term financial instruments. The cost of these
investments approximates fair value.
Marketable Securities -
Marketable securities are stated at fair value.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts -
The Company provides an allowance for doubtful accounts
and notes receivable based on the aggregate estimated
collectibility of the receivables.
Inventory Valuation -
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market, cost
being determined by the average cost method, except for
materials in transit which are stated at actual cost as
determined by the specific identification method.
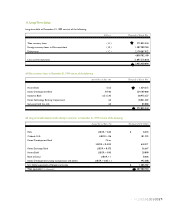
Property, Plant and Equipment and Related Depreciation -
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost, except for
certain assets subject to upward revaluation in accordance
with the Asset Revaluation Law of Korea. The revaluation
presents production facilities and other buildings at their
depreciated replacement cost, and land at the prevailing
market price, as of the effective date of revaluation. The
revaluation increment, net of revaluation tax, is first applied to
offset accumulated deficit and deferred foreign exchange
losses, if any. The remainder may be credited to other capital
surplus or transferred to common stock. A new basis for
calculating depreciation is established for revalued assets (see
Note 8).
Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method,
based on the estimated useful lives of the assets as described
below.
Estimated
Useful Lives in Years
Buildings and auxiliary facilities 7 - 60
Machinery and equipment 2 - 10
Tools and fixtures 2 - 10
Structures and others 2 - 40
The Company capitalizes interest expense incurred on
borrowings used to finance the cost of constructing facilities
and equipment (see Note 8).
Maintenance and Repairs -
Routine maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as
incurred. Expenditures which enhance the value or extend the
useful life of the related assets are capitalized.
Equity Investments in Subsidiaries and Affiliated Companies &
Other Investments -
All investments in equity and debt securities are initially
carried at cost, including incidental expenses. The subsequent
accounting for investments by the type of security is as
follows.
Investments in marketable equity securities of non-controlled
investees, classified as other investments, are carried at fair
value. Temporary changes in fair value are accounted for in the
capital adjustment account, a component of stockholders'
equity. Declines in fair value which are anticipated to be
permanent are recorded in current operations after
eliminating any previously recorded capital adjustment for
temporary changes. Subsequent recoveries or other future
changes in fair value are recorded in the capital adjustment
account.
Investments in non-marketable equity securities of non-
controlled investees, classified as other investments, are
carried at cost, except for declines in the Company’s
proportionate ownership of the underlying book value of the
invested company which are anticipated to be permanent,
which are recorded in current operations. Subsequent
recoveries are also recorded in current operations up to the
original cost of the investments.
Investments in equity securities of companies over which the
Company exerts significant control or influence, classified as
equity investments in subsidiaries and affiliated companies, are
recorded using the equity method of accounting. Differences
between the initial purchase price and the Company's initial
proportionate ownership of the net book value of the invested
company are amortized over 5 years using the straight-line
method. Under the equity method, the Company records
changes in its proportionate ownership of the book value of
the invested company as current operations, capital
adjustments or adjustments to retained earnings, depending on
the nature of the underlying change in book value of the
invested company.
50001010010100101