Dell 1999 Annual Report Download - page 27
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 27 of the 1999 Dell annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.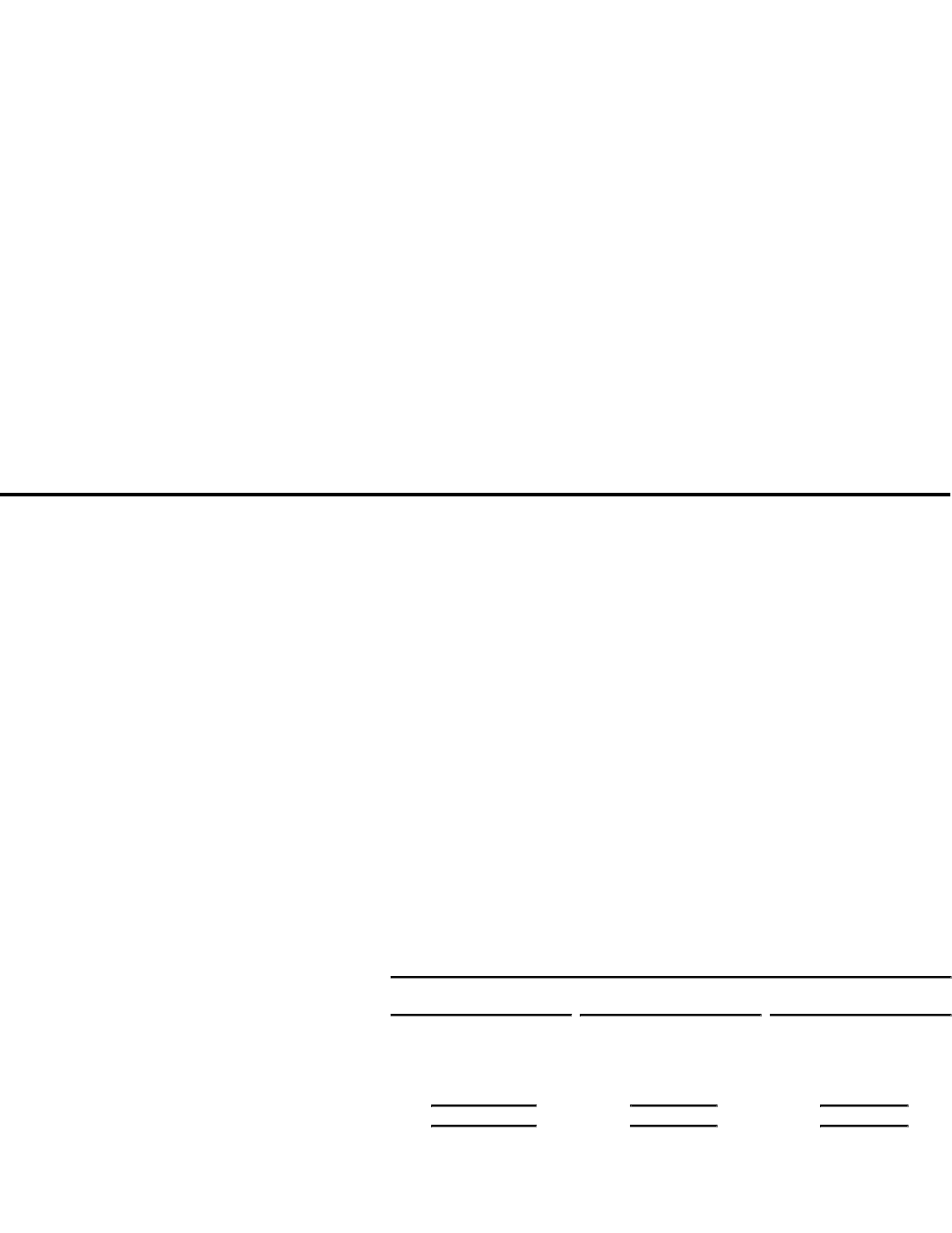
were not material. Gross unrealized gains on January 28, 2000 were $879 million. Gross unrealized losses on January 28, 2000 were
$13 million. Gross unrealized gains and losses at January 29, 1999 were not material.
Foreign Currency Instruments
The Company uses foreign currency purchased option contracts to reduce its exposure to currency fluctuations involving probable
anticipated, but not firmly committed, transactions. It also uses forward contracts to reduce exposure to transactions with firm foreign
currency commitments. These transactions include international sales by U.S. dollar functional currency entities, foreign currency
denominated purchases of certain components and intercompany shipments to certain international subsidiaries. The risk of loss
associated with purchased options is limited to premium amounts paid for the option contracts. Foreign currency purchased options
generally expire in 12 months or less. At January 28, 2000, the Company held purchased option contracts with a notional amount of
$2 billion, a net asset value of $75 million and a combined net realized and unrealized deferred gain of $5 million. At January 29,
1999, the Company held purchased option contracts with a notional amount of $1 billion, a net asset value of $48 million and a
combined net realized and unrealized deferred loss of $21 million. The risk of loss associated with forward contracts is equal to the
exchange rate differential from the time the contract is entered into until the time it is settled. Transactions with firm foreign currency
commitments are generally hedged using foreign currency forward contracts for periods not exceeding three months. At January 28,
2000, the Company held forward contracts with a notional amount of $818 million, a net asset value of $17 million and a net realized
and unrealized deferred gain of $490 million. At January 29, 1999, the Company held forward contracts with a notional amount of
$1 billion, a net liability value of $24 million and a combined net realized and unrealized deferred gain of $1 million.
Long-term Debt and Interest Rate Risk Management
In April 1998, the Company issued $200 million 6.55% fixed rate senior notes due April 15, 2008 (the "Senior Notes") and
$300 million 7.10% fixed rate senior debentures due April 15, 2028 (the
37
"Senior Debentures"). Interest on the Senior Notes and Senior Debentures is paid semi-annually. The Senior Notes and Senior
Debentures are redeemable, in whole or in part, at the election of the Company for principal, any accrued interest and a redemption
premium based on the present value of interest to be paid over the term of the debt agreements. The Senior Notes and Senior
Debentures generally contain no restrictive covenants, other than a limitation on liens on the Company's assets and a limitation on
sale-leaseback transactions.
Concurrent with the issuance of the Senior Notes and Senior Debentures, the Company entered into interest rate swap agreements
converting the Company's interest rate exposure from a fixed rate to a floating rate basis to better align the associated interest rate
characteristics to its cash and investments portfolio. The interest rate swap agreements have an aggregate notional amount of
$200 million maturing April 15, 2008 and $300 million maturing April 15, 2028. The floating rates are based on three-month London
interbank offered rates ("LIBOR") plus .41% and .79% for the Senior Notes and Senior Debentures, respectively. As a result of the
interest rate swap agreements, the Company's effective interest rates for the Senior Notes and Senior Debentures were 6.01% and
6.34%, respectively, for fiscal year 2000.
The Company has designated the issuance of the Senior Notes and Senior Debentures and the related interest rate swap agreements as
an integrated transaction. Accordingly, the differential to be paid or received on the interest rate swap agreements is accrued and
recognized as an adjustment to interest expense as interest rates change.
The difference between the Company's carrying amounts and fair value of its long-term debt and related interest rate swaps was not
material at January 28, 2000 and January 29, 1999.
NOTE 4 — Income Taxes
The provision for income taxes consists of the following:
Fiscal Year Ended
January 28, January 29, February 1,
2000 1999 1998
(in millions)
Current:
Domestic $ 1,008 $ 567 $ 362
Foreign 84 86 41
Deferred (307) (29) 21
Provision for income taxes $ 785 $ 624 $ 424
Income before income taxes and extraordinary loss included approximately $449 million, $529 million, and $309 million related to
foreign operations in fiscal years 2000, 1999, and 1998, respectively.
The Company has not recorded a deferred income tax liability of approximately $541 million for additional taxes that would result
from the distribution of certain earnings of its foreign subsidiaries if they were repatriated. The Company currently intends to reinvest
indefinitely these undistributed earnings of its foreign subsidiaries.