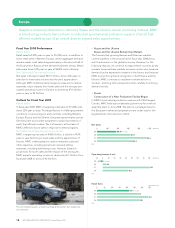
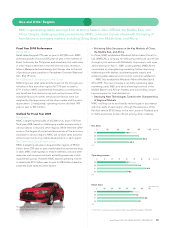
Mitsubishi 2009 Annual Report Download - page 22
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 22 of the 2009 Mitsubishi annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.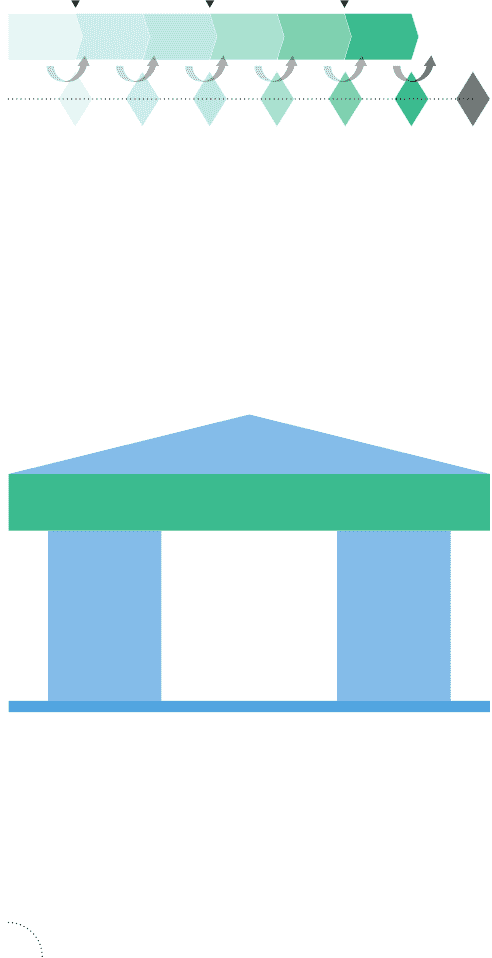
F E D C B A Z
Quality
Building in Development/Manufacturing Quality
• Mitsubishi Motors Development System (MMDS)
MMC has introduced the Mitsubishi Motors Development System
(MMDS), which is centered on the concept of quality gates (QGs)
in every product development process. MMDS is a comprehen-
sive quality management system that sets and assesses/evaluates
the achievement of specific performance benchmarks for every
quality gate at each stage of operations, from vehicle planning to
sales and after-sales services. MMC has adopted a methodology
of advancing to the next stage of operations only after confirm-
ing the achievement of benchmarks for each quality gate using
this decision-making system.
• Mitsubishi Motors Production Way (MMPW)
MMC has established a unified global quality assurance frame-
work by introducing the Mitsubishi Motors Production Way
(MMPW), MMC’s concept and philosophy of manufacturing, to its
plants around the world. One of the basic concepts is to achieve
rigorous quality assurance in each work stage through the incor-
poration of “stage completion” (only allowing non-defective units
to pass to the next stage).
MMC is developing various quality assurance systems to ensure that customers can drive its vehicles with
peace of mind.
Human Assets* Development
Building quality products starts with building quality people.
Based on this approach, MMC provides practical, in-house train-
ing to enhance the quality of human assets through quality engi-
neering, Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Fault Tree
Analysis (FTA).
Rapid Feedback of Customer Information
• New Quality Information Management System (SQM-BC)
MMC introduced the SQM-BC in 2006 to allow MMC to swiftly
respond to quality-related information from customers. The
SQM-BC manages consolidation of multiple after-service related
systems. The DES (Data Entry System), one of the core systems,
enables sharing of quality-related information from customers
between MMC and distributors to be received in real time, making
possible the further facilitation of the analysis and solution of qual-
ity issues and the sharing of information among distributors.
The WAS (Warranty Analysis System), another core system,
enables the detailed analysis of statistics for complaint data by
model, part, production date and other parameters. This informa-
tion can be effectively utilized by the design, manufacturing, service,
and other related departments to quickly respond to complaints.
WAS entered service at plants around the world in 2009.
• Timely and Transparent Determination Process for Recalls
and Other Issues
Since the recall issue of 2004, MMC has taken diligent steps to
restore confidence, including discussions with outside experts.
MMC has established standardized, strict criteria for determining
recalls, and added members with more of a customer’s perspec-
tive to recall judgment meetings including those from the Cus-
tomer Relations Department and labor union members. MMC
has created a more open system by reporting the meeting’s
deliberations to top management for final decision. The transpar-
ency of these proceedings is ensured through monitoring by the
CSR Promotion Office.
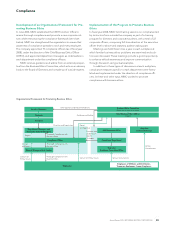
Quality Management Structure
MMC acquired ISO 9002 certification at the plant level in 1997,
and ISO 9001 certification for the entire company in 2003, cover-
ing a range of operations from development to sales and after-
sales services. This includes technical centers located nationwide,
from Hokkaido to Kyushu. These certifications reflect the con-
certed efforts of MMC staff to improve quality management
based on the philosophy of putting the customer first.
Notes:
* MMC uses the term “human assets” because it sees people as key assets.
Start of development Design approval Market launch
Product
planning
Design
concept
Design
specifications
Prototype
testing
Completion
of
development
Mass production
and quality
verification
Start of mass
production
Gate
MMDS (Mitsubishi Motors Development System)
Basic Concepts of MMPW
Fundamental manufacturing principle:
build quality goods inexpensively and efficiently
Stage
completion
Eliminate
overburden-
ing, redun-
dancy and
inefficiency
Customer Satisfaction
20 MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORPORATION Annual Report 2009