Olympus 2010 Annual Report Download - page 58
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 58 of the 2010 Olympus annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
56 OLYMPUS 2010
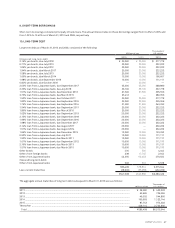
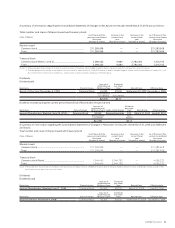
Amounts of lease receivables and leased investment assets to be collected after the consolidated closing date
(As of March 31, 2010) Millions of yen
Due in One Year
or Less
Due after One
Year through Two
Years
Due after Two
Years through
Three Years
Due after Three
Years through
Four Years
Due after Four
Years through
Five Years
Due after Five
Years
Current Assets
Lease receivable ........................................ ¥ — ¥ — ¥ — ¥ — ¥ — ¥ —
Lease investment assets............................ 13,725 37 37 29 10 —
Investment and Other Assets
Lease receivable ........................................ — — — — — —
Lease investment assets............................ —9,450 5,684 1,140 346 177
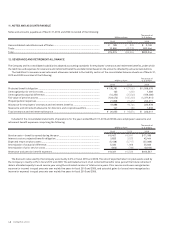
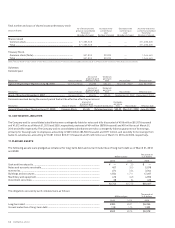
(As of March 31, 2009) Millions of yen
Due in One Year
or Less
Due after One
Year through Two
Years
Due after Two
Years through
Three Years
Due after Three
Years through
Four Years
Due after Four
Years through
Five Years
Due after Five
Years
Current Assets
Lease receivable ........................................ ¥ — ¥ — ¥ — ¥ — ¥ — ¥ —
Lease investment assets............................ 13,609 21 21 21 12 —
Investment and Other Assets
Lease receivable ........................................ — — — — — —
Lease investment assets............................ —8,756 5,402 1,791 610 139
(As of March 31, 2010) Thousands of U.S. dollars
Due in One Year
or Less
Due after One
Year through Two
Years
Due after Two
Years through
Three Years
Due after Three
Years through
Four Years
Due after Four
Years through
Five Years
Due after Five
Years
Current Assets
Lease receivable ......................................... $ — $ — $ — $ — $ — $ —
Lease investment assets ............................ 152,500 411 411 322 111 —
Investment and Other Assets
Lease receivable ......................................... — — — — — —
Lease investment assets ............................ —105,000 63,156 12,667 3,844 1,967
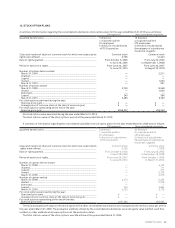
Future minimum lease payments under the non-cancelable operating leases having remaining terms in excess of one year were as follows:
(As of March 31, 2010) Millions of yen Thousands of U.S. dollars
Due in One Year
or Less
Due after One
Year
Total minimum
lease payments
Due in One Year
or Less
Due after One
Year
Total minimum
lease payments
¥658 ¥146 ¥804 $7,311 $1,622 $8,933
(As of March 31, 2009) Millions of yen
Due in One Year
or Less
Due after One
Year
Total minimum
lease payments
¥932 ¥565 ¥1,497
25. DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The Company and its consolidated subsidiaries use derivative financial instruments in the normal course of their business to manage
the exposure to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates and interest rates. The primary classes of derivatives used by the Company and
its consolidated subsidiaries are foreign exchange forward contracts, currency options, currency swaps and interest rate swaps. Almost
all derivative transactions are used to hedge interest rates and foreign currency positions in connection with their business. Accordingly,
market risk in these derivatives is largely offset by opposite movements in the underlying positions. Management assesses derivative
transactions and market risks surrounding these transactions according to the Company’s policy regarding derivative transactions.
Contracts of derivative financial instruments are executed by finance departments of the Company or subsidiaries.
The Company’s and its consolidated subsidiaries’ trade payable that are denominated in foreign currencies which meet specific
matching criteria and have been hedged by foreign exchange forward contracts are translated at the foreign exchange rate stipulated in the
contracts (special hedge accounting for foreign exchange forward contracts).
Interest rate swaps that quality for hedge accounting and meet specific matching criteria are not remeasured at market value, but the
differential to be paid or received under the swap agreements are accrued and included in interest expense or income (special hedge
accounting short-cut method for interest rate swaps).