Medtronic 2008 Annual Report Download - page 3
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 3 of the 2008 Medtronic annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
• To contribute to human welfare by application
• To direct our growth in the areas of biomedical
• To strive without reserve for the greatest possible
• To make a fair profit on current operations to meet
• To recognize the personal worth of employees by
• To maintain good citizenship as a company.
• Een bijdrage leveren aan het welzijn van de
passen bij onderzoek, ontwerp, fabricage en verkoop
van instrumenten of apparaten die pijn verlichten,
• Onze groei richten op die gebieden van de
bijeenbrengen die bijdragen tot de uitbreiding
het mijden van gebieden waaraan we geen unieke
en waardevolle bijdrage kunnen leveren.
• Onvoorwaardelijk streven naar de hoogst
mogelijke betrouwbaarheid en kwaliteit van onze
producten; het ongeëvenaarde voorbeeld zijn en
door anderen erkend te worden als een bedrijf
dat staat voor toewijding, eerlijkheid, integriteit en
• Een redelijke winst maken uit de huidige
en onze doelstellingen kunnen verwezenlijken.
• De individuele bijdrage van werknemers erkennen
d.m.v. een werkstructuur waarbij persoonlijke
van het bedrijf te delen, mogelijk zijn.
• Zich als bedrijf maatschappelijk verantwoord
blijven gedragen.
• Contribuire al benessere umano applicando
• Dirigere la nostra crescita nelle aree della
• Sforzarci senza riserve di raggiungere l’affidabilità
• Ricavare un equo profitto dalle attività correnti in
• Riconoscere il valore personale dei dipendenti
• Mantenere una presenza sociale come azienda.
• Contribuir al bienestar del hombre aplicando
• Encauzar nuestro crecimiento hacia las especialidades
• Esforzarnos todo lo posible para alcanzar la
• Lograr una rentabilidad adecuada para las
objetivos.
• Reconocer el valor individual de nuestros
empleados ofreciéndoles un ambiente de trabajo
• Contribuir como empresa al bienestar de la
•
• Orienter notre croissance vers les secteurs
• Tout mettre en œuvre et s’investir à fond pour
• Dégager un profit raisonnable de nos activités pour
taux de croissance et atteindre nos objectifs.
• Reconnaître la valeur personnelle des employés et
• Remplir nos responsabilités civiques en tant
• Einen Beitrag zum Wohle der Menschen zu leisten
• Erfolgsorientiertes Wachstum dort, wo wir stark
sind, im Bereich der biomedizinischen Technik.
Kein Engagement in Bereichen, in denen wir keine
wesentlichen und wertvollen Beiträge leisten
• Kompromisslose Zuverlässigkeit und Qualität
• Profitabel zu wirtschaften, um unsere Verpflichtung
Ziele zu realisieren.
• Anerkennung des Wertes und der Leistungen jedes
Zufriedenheit unserer Mitarbeiter beitragen, z. B.
Beteiligung am Unternehmenserfolg.
• Als verantwortungsbewusstes Mitglied der
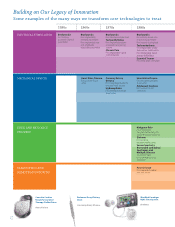
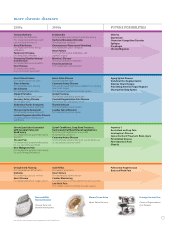
Innovative Therapies Changing the Way People Live with Chronic Disease
* Still in development or not yet cleared/approved for marketing in the United States.
Cardiac Rhythm Disorders
1 Irregular Heart Rates
Implantable pacemakers that regulate slow heart rates, and implantable and
external defibrillators to regulate or shock fast heart rates that can lead to
sudden cardiac arrest.
2 Heart Failure
Implantable cardiac resynchronization systems that resynchronize the heart
and improve blood-pumping ability.
3 Unexplained Fainting
Implantable recorders that help diagnose heart-related causes of recurrent,
unexplained fainting.
Cardiovascular Diseases
4 Coronary Artery Disease
Implantable stents, as well as diagnostic and guiding catheters and angioplasty
balloons, to open blocked arteries; and perfusion systems for arrested-heart
surgery and heart stabilization systems for beating-heart surgery to bypass
blocked arteries to improve blood supply to the heart.
5 Heart Valve Disease
Implantable bioprosthetic tissue and mechanical valves to replace damaged
valves.
6 Atrial Fibrillation*
Radio frequency ablation systems that inhibit abnormal electrical activity.
7 Aortic Disease
Implantable endovascular stent grafts that provide support for a weakened and
ballooning aorta, which runs through the chest and abdomen, and distributes
blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
8 Peripheral Vascular Disease*
Catheters and implantable stents that treat blood vessel and duct blockages in
other parts of the body.
Spinal Conditions and Musculoskeletal Trauma
9 Cervical Herniated Disc
Artificial disc that functions like a joint to provide neck mobility.
10 Scoliosis
Fusion systems that correct and stabilize abnormal spinal curves.
11 Degenerative Disc Disease
Minimal Access Spinal Technologies (MAST) and bone morphogenetic proteins
that treat painful conditions of the spine; surgical imaging systems to enable
advanced visualization of the spinal anatomy; and a catheter system to identify
disc pain sources.
12 Spinal Fracture
Balloon kyphoplasty that lifts fractured bone and fills the cavity with cement
to stabilize fractured vertebra.
13 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Interspinous process spacers to enlarge space between bones and reduce
pressure on affected nerves.
14 Sinus Augmentation
Bone morphogenetic proteins that augment bone growth for missing or
damaged bone in the face.
15 Tibial Fractures
Bone morphogenetic proteins that heal certain types of fractured shin bones.
Ear, Nose and Throat Conditions
16 Ménière’s Disease
Portable external device that delivers low-pressure air pulses to the inner ear to
alleviate severe vertigo.
17 Otitis Media
Surgical tools and implantable devices to remove and replace excess or diseased
tissue in the ear.
18 Sinusitis
Surgical tools to unblock clogged or obstructed sinuses.
19 Thyroid Disease
Equipment that monitors nerves during complicated, high-risk thyroid surgery
to avoid nerve damage.
Neurological Disorders
20 Parkinson’s Disease, Essential Tremor and Dystonia
Implantable deep brain stimulation systems to reduce motor symptoms of
movement disorders.
21 Hydrocephalus
Implantable shunts that divert excess fluid in the brain to other parts of the
body, where it can be re-absorbed; and neuronavigation systems that enable
advanced visuals of the brain.
22 Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder*
Implantable deep brain stimulation systems to lessen symptoms, including
obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
23 Depression*
Implantable deep brain stimulation systems to lessen symptoms, including
profound and persistent sadness, and suicidal thoughts.
24 Severe Spasticity Associated with Multiple Sclerosis, Cerebral
Palsy, Stroke, Spinal Cord and Head Injuries
Implantable infusion systems that deliver medication directly to the intrathecal
space—the fluid-filled area surrounding the spinal cord—to loosen tight,
stiff muscles.
25 Epilepsy*
Implantable deep brain stimulation systems to reduce the frequency of seizures.
26 Chronic Pain, Cancer Pain and Painful Neuropathy
Implantable neurostimulation systems and infusion systems that deliver
electrical pulses and drugs, respectively, to specific areas of the body—usually
around the spine—to block pain sensations. Non-opioid medication* for the
implantable infusion systems.
27 Chronic Migraine*
Implantable neurostimulation systems that deliver electrical pulses to the
occipital nerves at the back of the head for chronic, intractable migraine.
Urological and Digestive Disorders
28 Overactive Bladder and Urinary Retention
Implantable neurostimulation system targeting the sacral nerves to control
bladder function.
29 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Radio frequency ablation system that delivers treatment directly to the prostate
to reduce excess tissue and improve urine flow.
30 Acid Reflux
Diagnostic test that uses a wireless capsule to monitor pH levels in the
esophagus.
31 Gastroparesis
Implantable gastric stimulation system to minimize the chronic nausea and
vomiting associated with abnormally slow digestion.
32 Fecal Incontinence*
Implantable neurostimulation system targeting the sacral nerves to control
bowel function.
Diabetes
33 Diabetes
External and implantable insulin pumps, real-time continuous glucose
monitoring systems and therapy management software that help diabetes
patients improve blood sugar control.