Tesco 2004 Annual Report Download - page 12
Download and view the complete annual report
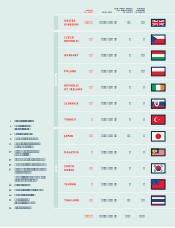
Please find page 12 of the 2004 Tesco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.10 TESCO PLC
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE CONTINUED
by objectives that are derived from the business plan. The plan
covers both revenue and capital expenditure and forms the
basis of business plans for all our business entities. From this
the Board, together with monitoring regimes based upon our
Steering Wheel, agrees the annual revenue and capital budgets.
The Steering Wheel is the term used to describe our balanced
scorecard approach, which we believe is the best way to achieve
results for our shareholders. It sets out a broad range of targets
under quadrant headings of customers, operations, people and
finance. This allows the business to be operated and monitored
on a balanced basis with due regard for all stakeholders. The
Executive Committee undertakes a formal review of progress
on a quarterly basis and any resulting actions considered
appropriate are communicated throughout the business.
The capital investment programme is subject to formalised review
procedures requiring key criteria to be met. All major initiatives
require business cases to be prepared, normally covering a
minimum period of five years. Post-investment appraisals are
also carried out.
Risk management process At the highest level, the Board
considers strategic risk every time it meets. The two-day Board
Conference, referred to earlier, considers where future
opportunities and risks lie and helps shape our corporate strategy
going forward. Accountabilities for managing operational risks are
clearly assigned to line management. Internal controls have been
developed over all risks in line with the risk appetite determined
by the Board and are subject to review. Formal risk assessments
are carried out routinely throughout the UK and international
businesses. Procedures exist to ensure that significant risks and
control failures are escalated to senior management and the
Board, as necessary, on a daily, weekly and periodic basis.
Monitoring The monitoring of strategic and operational risks is
the responsibility of the Board and line managers respectively.
The Board maintains the Key Risk Register and considers during
formal risk assessments whether the actions being taken in
mitigation are sufficient.
The internal audit function also operates on a risk-based
approach, helping managers with their risk responsibilities and
advising on appropriate controls.
Annual statements received from CEOs further support the
monitoring of key subsidiary operations. These statements
confirm that the Boards governance policies have been adopted
in practice and spirit.
Overall, the Audit Committee seeks to ensure that the whole
management process provides adequate control over all major
risks to the Group. This is achieved through consideration of
regular reports from internal and external audit, alongside
discussions with senior managers.
Other specialist functions within the Group, notably Trading Law
and Technical and Company Secretariat, provide assurance and
advice on health and safety, regulatory and legal compliance and
social, ethical and environmental issues (SEE).These functions report
their findings on a regular basis to the Compliance Committee.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, the companys external auditors,
contribute a further independent perspective on certain aspects
of the internal financial control system arising from their work.
Independence is strengthened by the requirement to rotate
audit partners every five years. The engagement and
independence of auditors is considered annually by the Audit
Committee which recommends their selection to the Board.
Communication A programme of communication exists and is
constantly being developed to ensure that all staff are aware
of the parameters that constitute acceptable business
performance and the expectations of the Board in managing
risk. This provides clear definition of the Groups purpose and
goals, accountabilities and the scope of permitted activities of
companies, executive functions and individual staff.
Risks and opportunities The company manages a broad range
of Þnancial and non-Þnancial risks, including those relating to CSR
responsibilities. The construction of the Key Risk Register takes
into account matters raised in the CSR assessment. In the Boards
view, there are sufÞcient controls in place to manage SEE risks.
Customer focus is fundamental to delivering the overall strategy
and the way risk is managed. Business practices centre on serving
the customer and in meeting those challenges the company
recognises its responsibility to deliver safe, quality products at
the right price.
All companies have to face ethical dilemmas in the normal course
of business and the companys approach comes from the Tesco
Values. The Values set out the standards that the Board wish to
uphold in how it treats its people. These are supported by
Codes of Ethics and govern the relationships between the
company and employees, suppliers and contractors. The
Compliance Committee regularly monitors adherence to these
codes. The company is a signatory to the DTI Code of Conduct
and has met fully its obligations for implementing the Code.