Starbucks 2007 Annual Report Download - page 54
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 54 of the 2007 Starbucks annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
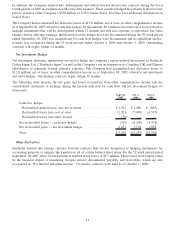
The following tables present the length of time available-for-sale securities were in continuous unrealized loss
positions but were not deemed to be other-than-temporarily impaired (in thousands):
Consecutive monthly unrealized losses
Gross
Unrealized
Holding
Losses
Fair
Value
Gross
Unrealized
Holding
Losses
Fair
Value
Less Than 12 Months
Greater Than
or Equal to 12 Months
September 30, 2007
State and local government obligations ............ $— $ — $ (21) $ 5,795
Total ..................................... $— $ — $ (21) $ 5,795
October 1, 2006
State and local government obligations ............ $— $ — $(414) $49,960
Corporate debt securities ....................... (2) 2,486 — —
Total ..................................... $(2) $2,486 $(414) $49,960
Gross unrealized holding losses of $21 thousand for greater than or equal to twelve months as of September 30,
2007, pertained to two fixed income securities, specifically state and local government obligations, and were
primarily caused by interest rate increases subsequent to the date of purchase. The contractual terms of these
securities do not permit the issuer to settle at a price less than the par value of the investment, which is the equivalent
of the amount due at maturity. These securities had a minimum credit rating of “A+.” Since Starbucks has the ability
and intent to hold these securities until a recovery of fair value, which may be at maturity, and because the
unrealized losses were primarily due to higher interest rates subsequent to the date of purchase, the Company does
not consider these securities to be other-than-temporarily impaired.
There were no realized losses recorded for other than temporary impairments during fiscal years 2007, 2006 or
2005.
Trading securities are comprised mainly of marketable equity mutual funds that approximate a portion of the
Company’s liability under the Management Deferred Compensation Plan (“MDCP”), a defined contribution plan.
The corresponding deferred compensation liability of $86.4 million in fiscal 2007 and $64.6 million in fiscal 2006 is
included in “Accrued compensation and related costs” on the consolidated balance sheets. In fiscal years 2007 and
2006, the changes in net unrealized holding gains/losses in the trading portfolio included in earnings were a net gain
of $7.5 million and a net loss of $4.2 million, respectively.
Long-term investments generally mature in less than two years.
Note 4: Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company may engage in transactions involving various derivative instruments, with maturities generally not
longer than five years, to hedge interest rates, commodity prices, and foreign currency denominated revenues,
purchases, assets and liabilities.
Cash Flow Hedges
The Company and certain subsidiaries enter into cash flow derivative instruments to hedge portions of anticipated
revenue streams and inventory purchases in currencies other than the entity’s functional currency. Outstanding
forward contracts, which comprise the majority of the Company’s derivative instruments, hedge monthly forecasted
revenue transactions denominated in Japanese yen and Canadian dollars, as well as forecasted inventory purchases
denominated primarily in U.S. dollars for foreign operations. The Company also has futures contracts to hedge the
variable price component for a small portion of its price-to-be-fixed green coffee purchase contracts.
52