Apple 2004 Annual Report Download - page 81
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 81 of the 2004 Apple annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
The Company may enter into foreign currency forward contracts to hedge the translation and economic exposure of a net investment position in
a foreign subsidiary. The Company may also enter into foreign currency forward and option contracts to offset the foreign exchange gains and
losses generated by the remeasurement of certain recorded assets and liabilities in non-functional currencies. Changes in the fair value of these
derivatives are recognized in current earnings in other income and expense as offsets to the changes in the fair value of the related assets or
liabilities. Due to market movements, changes in option time value can lead to increased volatility in other income and expense.
Interest Rate Risk Management
From time to time, the Company historically entered into interest rate derivative transactions with financial institutions in order to better match
the Company's floating-rate interest income on its cash equivalents and short-term investments with its fixed-rate interest expense on any
outstanding long-term debt, and/or to diversify a portion of the Company's exposure away from fluctuations in short-term U.S. interest rates.
In prior years, the Company had entered into interest rate debt swaps with financial institutions in order to better match the Company's floating-
rate interest income on cash equivalents and short term investments with its fixed rate interest expense on its long term debt, and/or to diversify a
portion of the Company's exposure away from fluctuations in short term U.S. interest rates. The interest rate swaps required the Company to pay
a floating interest rate based on the three- or six-month U.S. dollar LIBOR and receive a fixed rate of interest without exchanges of the
underlying notional amounts. These swaps effectively converted the Company's fixed-rate 10-year debt to floating-rate debt. Due to prevailing
market interest rates, during 2001 and 2002 the Company entered into and then subsequently closed out interest rate debt swap positions
realizing gains of $23 million which were deferred over the remaining life of the debt.
As of September 25, 2004 and September 27, 2003, the Company had no interest rate derivatives outstanding.
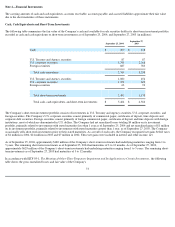
Debt
In February 2004, the Company retired $300 million of debt outstanding in the form of 6.5% unsecured notes. The notes were originally issued
in 1994 and were sold at 99.9925% of par for an effective yield to maturity of 6.51%. As of September 27, 2003, the carrying amount of these
notes, including unamortized deferred gains associated with closed debt interest rate swaps, was $304 million, respectively, while the fair value
was $302 million. The fair value of the notes was based on their listed market values as of September 27, 2003.
Non-Current Debt and Equity Investments and Related Gains and Losses
The Company has held significant investments in ARM Holdings plc (ARM), Akamai Technologies, Inc. (Akamai) and EarthLink Network, Inc.
(EarthLink). These investments have been reflected in the consolidated balance sheets as long term assets within other assets and have been
categorized as available-for-sale requiring that they be carried at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of taxes, reported in equity as a
component of accumulated other comprehensive income. All realized gains on the sale of these investments have been included in other income
and expense. In fiscal 2004, the Company sold all of its remaining non-current investments in public companies.
77