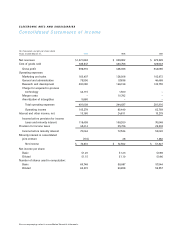
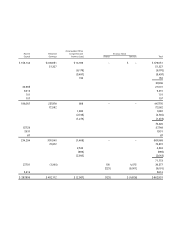
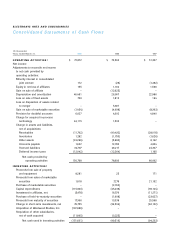
Electronic Arts 1999 Annual Report Download - page 32
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 32 of the 1999 Electronic Arts annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
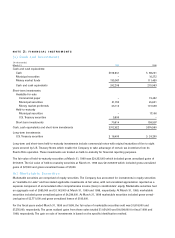
In March 1998, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (“AICPA”) issued SOP 98-1, “Accounting for the
Costs of Computer Software Developed or Obtained for Internal Use.” SOP 98-1 requires that certain costs related to
the development or purchase of internal-use software be capitalized and amortized over the estimated useful life of
the software. SOP 98-1 is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 1998.
The adoption of SOP 98-1 is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s results of operations.
In December 1998, the Accounting Standards Executive Committee of the AICPA issued SOP 98-9, “Software Revenue
Recognition, with Respect to Certain Arrangements,” which required recognition of revenue using the “residual method”
in a multiple element arrangement when fair value does not exist for one or more of the undelivered elements in the
arrangement. SOP 98-9 is effective for transactions entered into after March 15, 1999. Under the “residual method,”
the total fair value of the undelivered elements is deferred and subsequently recognized in accordance with SOP 97-2.
The Company will adopt SOP 98-9 in fiscal year 2000 and does not expect a material change to its accounting for
revenues as a result of the provisions of SOP 98-9.
(p) Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management
to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent
assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during
the reporting period. Such estimates include provisions for doubtful accounts, sales returns and allowances, warranty
provisions, and estimates regarding the recoverability of prepaid royalty advances and inventories. Actual results could
differ from those estimates.
(q) Reclassifications
Certain amounts have been reclassified to conform to fiscal 1999 presentation.
(r) Long-Lived Assets
The Company evaluates long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangibles for impairment whenever events or changes
in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets is mea-
sured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future net cash flows expected to be generated by the asset.
If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the
carrying amount of the asset exceeds its fair value.