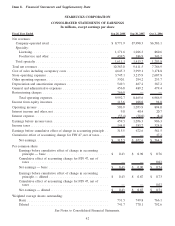
Starbucks 2008 Annual Report Download - page 53
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 53 of the 2008 Starbucks annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.balances at certain banks, which creates book overdrafts. Book overdrafts are presented as a current liability in
“Accounts payable” on the consolidated balance sheets.
Short-term and Long-term Investments
The Company’s short-term and long-term investments consist primarily of investment-grade debt securities as well
as bond and equity mutual funds, all of which are classified as available-for-sale or trading. As of September 28,
2008, a substantial portion of the Company’s available-for-sale investments consisted of auction rate securities, as
described in more detail in Note 4. Trading securities are recorded at fair value with unrealized holding gains and
losses included in net earnings. Available-for-sale securities are recorded at fair value, and unrealized holding gains
and losses are recorded, net of tax, as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income.
Available-for-sale securities with remaining maturities of less than one year and those identified by management at
time of purchase for funding operations in less than one year are classified as short-term, and all other available-for-
sale securities are classified as long-term. Unrealized losses are charged against net earnings when a decline in fair
value is determined to be other than temporary. Management reviews several factors to determine whether a loss is
other than temporary, such as the length of time a security is in an unrealized loss position, the extent to which fair
value is less than amortized cost, the impact of changing interest rates in the short and long term, the financial
condition and near term prospects of the issuer and the Company’s intent and ability to hold the security for a period
of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value. Realized gains and losses are accounted for on
the specific identification method. Purchases and sales are recorded on a trade date basis.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying value of cash and cash equivalents approximates fair value because of the short-term maturity of those
instruments. The fair value of the Company’s investments in marketable debt and equity securities, as well as bond
and equity mutual funds, is based upon the quoted market price on the last business day of the fiscal year. For equity
securities of companies that are privately held, or where an observable quoted market price does not exist, the
Company estimates fair value using a variety of valuation methodologies. Such methodologies include comparing
the security with securities of publicly traded companies in similar lines of business, applying revenue multiples to
estimated future operating results for the private company and estimating discounted cash flows for that company.
Declines in fair value below the Company’s carrying value deemed to be other than temporary are charged against
net earnings. For further information on investments, see Notes 4 and 7. The fair value of the Company’s debt is
estimated based on the quoted market prices for the same or similar issues or on the current rates offered to the
Company for debt of the same remaining maturities. The carrying value of short-term debt approximates fair value.
The estimated fair value of Starbucks $550 million of 6.25% Senior Notes was approximately $536 million.
Derivative Instruments
The Company manages its exposure to various risks within the consolidated financial statements according to an
umbrella risk management policy. Under this policy, Starbucks may engage in transactions involving various
derivative instruments, with maturities generally not longer than five years, to hedge interest rates, commodity
prices, and foreign currency denominated revenues, purchases, assets and liabilities.
The Company records all derivatives on the balance sheets at fair value. For a cash flow hedge, the effective portion
of the derivative’s gain or loss is initially reported as a component of other comprehensive income (“OCI”) and
subsequently reclassified into net earnings when the hedged exposure affects net earnings. For a net investment
hedge, the effective portion of the derivative’s gain or loss is reported as a component of OCI.
Cash flow hedges related to anticipated transactions are designated and documented at the inception of each hedge
by matching the terms of the contract to the underlying transaction. The Company classifies the cash flows from
hedging transactions in the same categories as the cash flows from the respective hedged items. Once established,
cash flow hedges are generally not removed until maturity unless an anticipated transaction is no longer likely to
occur. Discontinued or dedesignated cash flow hedges are immediately settled with counterparties, and the related
accumulated derivative gains or losses are recognized in “Interest income and other, net” on the consolidated
statements of earnings.
47