Ford 2013 Annual Report Download - page 108
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 108 of the 2013 Ford annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.106 Ford Motor Company | 2013 Annual Report
FORD MOTOR COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 14. RETIREMENT BENEFITS (Continued)
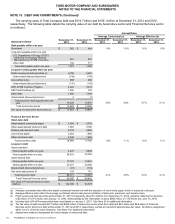
Pension Plan Asset Information
Investment Objective and Strategies. Our investment objectives for the U.S. plans are to minimize the volatility of the
value of our U.S. pension assets relative to U.S. pension liabilities and to ensure assets are sufficient to pay plan benefits.
As disclosed previously, in 2012 we adopted a broad global pension de-risking strategy, including a U.S. investment
strategy that increases the matching characteristics of our assets relative to our liabilities. Our U.S. target asset
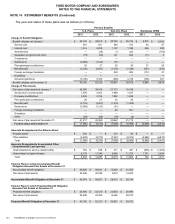
allocations, which we expect to reach over the next few years as the plans achieve full funding, are 80% fixed income and
20% growth assets (primarily alternative investments, which include hedge funds, real estate, private equity, and public
equity). Our largest non-U.S. plans (Ford U.K. and Ford Canada) have similar investment objectives to the U.S. plans.
We expect to reach similar target asset allocations for these plans as they achieve full funding over the next few years,
subject to legal requirements in each country.
Investment strategies and policies for the U.S. plans and the largest non-U.S. plans reflect a balance of risk-reducing
and return-seeking considerations. The objective of minimizing the volatility of assets relative to liabilities is addressed
primarily through asset - liability matching, asset diversification, and hedging. The fixed income target asset allocation
matches the bond-like and long-dated nature of the pension liabilities. Assets are broadly diversified within asset classes
to achieve risk-adjusted returns that in total lower asset volatility relative to the liabilities. Our rebalancing policies ensure
actual allocations are in line with target allocations as appropriate. Strategies to address the goal of ensuring sufficient
assets to pay benefits include target allocations to a broad array of asset classes, and strategies within asset classes that
provide adequate returns, diversification, and liquidity.
All assets are externally managed and most assets are actively managed. Managers are not permitted to invest
outside of the asset class (e.g., fixed income, public equity, alternatives) or strategy for which they have been appointed.
We use investment guidelines and recurring audits as tools to ensure investment managers invest solely within the
investment strategy they have been provided.
Derivatives are permitted for fixed income investment and public equity managers to use as efficient substitutes for
traditional securities and to manage exposure to interest rate and foreign exchange risks. Interest rate and foreign
currency derivative instruments are used for the purpose of hedging changes in the fair value of assets that result from
interest rate changes and currency fluctuations. Interest rate derivatives also are used to adjust portfolio duration.
Derivatives may not be used to leverage or to alter the economic exposure to an asset class outside the scope of the
mandate an investment manager has been given. Alternative investment managers are permitted to employ leverage
(including through the use of derivatives or other tools) that may alter economic exposure.
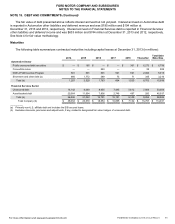
Significant Concentrations of Risk. Significant concentrations of risk in our plan assets relate to interest rate, equity,
and operating risk. In order to minimize asset volatility relative to the liabilities, a portion of plan assets is allocated to
fixed income investments that are exposed to interest rate risk. Rate increases generally will result in a decline in fixed
income assets while reducing the present value of the liabilities. Conversely, rate decreases will increase fixed income
assets, partially offsetting the related increase in the liabilities.
In order to ensure assets are sufficient to pay benefits, a portion of plan assets is allocated to growth assets that are
expected over time to earn higher returns with more volatility than fixed income investments which more closely match
pension liabilities. Within equities, risk is mitigated by constructing a portfolio that is broadly diversified by geography,
market capitalization, manager mandate size, investment style, and process. Within alternative investments, risk is
similarly mitigated by constructing a portfolio that is broadly diversified by asset class, investment strategy, manager, style,
and process.
Operating risks include the risks of inadequate diversification and weak controls. To mitigate these risks, investments
are diversified across and within asset classes in support of investment objectives. Policies and practices to address
operating risks include ongoing manager oversight (e.g., style adherence, team strength, firm health, and internal risk
controls), plan and asset class investment guidelines and instructions that are communicated to managers, and periodic
compliance and audit reviews to ensure adherence.
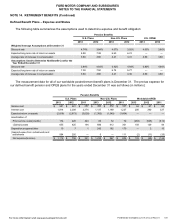
At year-end 2013, Ford securities comprised less than 1% of our plan assets.