Ford 2013 Annual Report Download - page 83
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 83 of the 2013 Ford annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Ford Motor Company | 2013 Annual Report 81
FORD MOTOR COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 3. ACCOUNTING STANDARDS ISSUED BUT NOT YET ADOPTED
Income Taxes - Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit When a Net Operating Loss Carryforward, a Similar Tax
Loss, or a Tax Credit Carryforward Exists. In July 2013, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued a new
accounting standard that requires an unrecognized tax benefit to be presented as a decrease in a deferred tax asset
where a net operating loss, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward exists and certain criteria are met. The new
accounting standard is effective as of January 1, 2014 and is consistent with our present practice.
Foreign Currency Matters - Parent’s Accounting for Cumulative Translation Adjustment. In March 2013, the FASB
issued a new accounting standard that clarifies the applicable guidance for a parent company’s accounting for the release
of the cumulative translation adjustment into net income upon derecognition of certain subsidiaries or groups of assets
within a foreign entity or of an investment in a foreign entity. The new accounting standard is effective as of
January 1, 2014 and is consistent with our present practice.
Liabilities - Obligations Resulting from Joint and Several Liability Arrangements. In February 2013, the FASB issued a
new accounting standard that provides guidance for the recognition, measurement, and disclosure of obligations resulting
from joint and several liability arrangements. This new accounting standard is effective as of January 1, 2014 and we do
not expect this standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements or financial statement
disclosures.
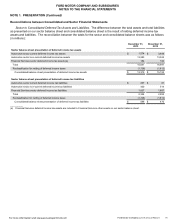
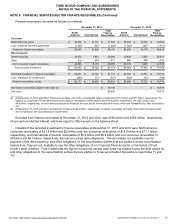
NOTE 4. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
Cash equivalents, marketable securities, and derivative financial instruments are presented on our financial
statements on a recurring basis at fair value, while other assets and liabilities are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring
basis, such as when we have an asset impairment.
Fair Value Measurements
In measuring fair value, we use various valuation methodologies and prioritize the use of observable inputs. The use
of observable and unobservable inputs and their significance in measuring fair value are reflected in our fair value
hierarchy assessment.
• Level 1 - inputs include quoted prices for identical instruments and are the most observable
• Level 2 - inputs include quoted prices for similar instruments and observable inputs such as interest rates,
currency exchange rates, and yield curves
• Level 3 - inputs include data not observable in the market and reflect management judgment about the
assumptions market participants would use in pricing the instruments
We review the inputs to the fair value measurements to ensure they are appropriately categorized within the fair value
hierarchy. Transfers into and transfers out of the hierarchy levels are recognized as if they had taken place at the end of
the reporting period.
Valuation Methodologies
Cash and Cash Equivalents. Included in Cash and cash equivalents are highly liquid investments that are readily
convertible to known amounts of cash, and which are subject to an insignificant risk of change in value due to interest
rate, quoted price, or penalty on withdrawal. A debt security is classified as a cash equivalent if it meets these criteria and
if it has a remaining time to maturity of three months or less from the date of acquisition. Amounts on deposit and
available upon demand, or negotiated to provide for daily liquidity without penalty, are classified as Cash and cash
equivalents. Time deposits, certificates of deposit, and money market accounts that meet the above criteria are reported
at par value on our balance sheet and are excluded from the tables below.
For more information visit www.annualreport.ford.com