American Airlines 2008 Annual Report Download - page 71
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 71 of the 2008 American Airlines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
68
6. Indebtedness (Continued)
In August 2008, AMR retired, by purchasing with cash, $75 million of the $300 million principal amount of the 4.25
percent senior convertible notes due 2023 (the 4.25 Notes). In September 2008, the remaining holders of the 4.25
Notes exercised their elective put rights and the Company purchased and retired these notes at a price equal to
100 percent of their principal amount, totaling $225 million. Under the terms of the 4.25 Notes, the Company had
the option to pay the purchase price with cash, stock, or a combination of cash and stock, and the Company
elected to pay for the 4.25 Notes solely with cash.
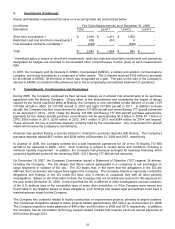
Certain debt is secured by aircraft, engines, equipment and other assets having a net book value of approximately
$10.5 billion as of December 31, 2008.
In 2008, the Company raised approximately $500 million under a loan secured by aircraft. The loan bears interest
at a LIBOR-based (London Interbank Offered Rate) variable rate with a fixed margin which resets quarterly and is
due in installments through 2015.
As of December 31, 2008, AMR has issued guarantees covering approximately $1.7 billion of American’s tax-
exempt bond debt and American has issued guarantees covering approximately $745 million of AMR’s unsecured
debt. In addition, as of December 31, 2008, AMR and American have issued guarantees covering approximately
$305 million of AMR Eagle’s secured debt, and AMR has issued guarantees covering an additional $2.1 billion of
AMR Eagle’s secured debt. In 2008, AMR issued guarantees covering $204 million of American’s leases of 39
Super ATR aircraft, which are subleased to AMR Eagle.
Cash payments for interest, net of capitalized interest, were $685 million, $861 million and $944 million for 2008,
2007 and 2006, respectively.
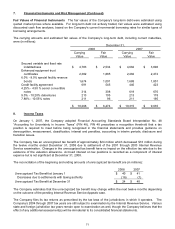
7. Financial Instruments and Risk Management
Fuel Price Risk Management In March of 2008, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards
No. 161, “Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, an amendment of FASB Statement
No. 133” (SFAS 161). SFAS 161 requires entities to provide greater transparency about how and why the entity
uses derivative instruments, how the instruments and related hedged items are accounted for under SFAS 133,
and how the instruments and related hedged items affect the financial position, results of operations, and cash
flows of the entity. The Company adopted SFAS 161 effective December 31, 2008.
FSP FIN 39-1, “Amendment of FASB Interpretation No. 39,” requires a reporting entity to elect a policy choice of
whether to offset rights to reclaim cash collateral or obligations to return cash collateral against derivative assets
and liabilities executed with the same counterparty, or present such amounts gross. The Company's accounting
policy is to present its derivative assets and liabilities gross including the collateral posted with or by the
counterparty.
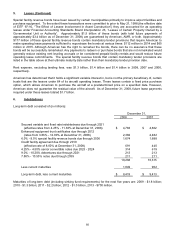
As part of the Company's risk management program, it uses a variety of financial instruments, primarily heating oil
option and collar contracts, as cash flow hedges to mitigate commodity price risk. The Company does not hold or
issue derivative financial instruments for trading purposes. As of December 31, 2008, the Company had fuel
derivative contracts outstanding covering 35 million barrels of jet fuel that will be settled over the next 24 months.
A deterioration of the Company’s liquidity position may negatively affect the Company’s ability to hedge fuel in the
future.