Safeway 2009 Annual Report Download - page 69
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 69 of the 2009 Safeway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SAFEWAY INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
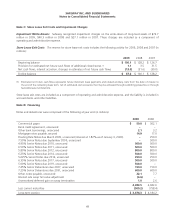
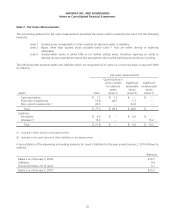
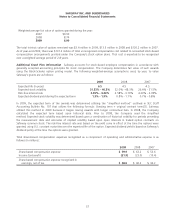
Annual Debt Maturities As of year-end 2009, annual debt maturities (principal payments only, excluding the interest
rate swap fair value adjustment and the unamortized deferred gain on swap termination) were as follows (in millions):
2010 $ 508.2
2011 502.8
2012 851.3
2013 1.4
2014 751.5
Thereafter 1,773.9
$ 4,389.1
Letters of Credit The Company had letters of credit of $54.3 million outstanding at year-end 2009, of which $47.2
million were issued under the credit agreement. The letters of credit are maintained primarily to support performance,
payment, deposit or surety obligations of the Company. The Company pays commissions ranging from 0.15% to 1.00%
on the face amount of the letters of credit.
Fair Value At year-end 2009 and year-end 2008, the estimated fair value of debt, including current maturities, was
$4.7 billion and $5.1 billion, respectively.
Note E: Financial Instruments
Safeway manages interest rate risk through the strategic use of fixed- and variable-interest rate debt and, from time to
time, interest rate swaps. The Company does not utilize financial instruments for trading or other speculative purposes,
nor does it utilize leveraged financial instruments.
Fair Value Hedges In December 2009, the Company effectively converted $800 million of its 5.80% fixed-rate debt
due 2012 to floating-rate debt through interest rate swap agreements. These interest rate swaps, under which the
Company agrees to pay variable rates of interest, are designated as fair value hedges of fixed-rate debt. The gain or loss
on the interest rate swap agreements, as well as the gain or loss on the debt being hedged, are recognized in current
earnings. Safeway includes the gain or loss on the fixed-rate debt in interest expense along with the offsetting loss or
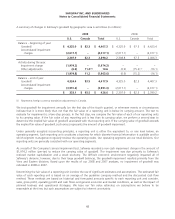
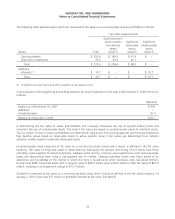
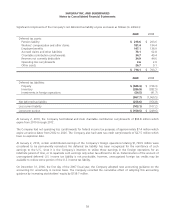
gain on the related interest rate swap as follows (in millions):
Income statement classification
Loss on interest
rate swaps
Gain on
debt
Interest expense $ (6.6) $ 6.6
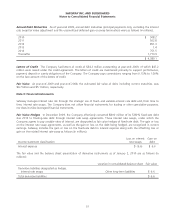
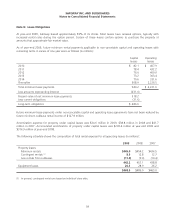
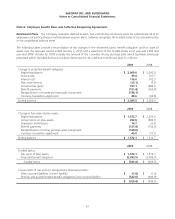
The fair value and the balance sheet presentation of derivative instruments as of January 2, 2010 are as follows (in
millions):
Location in consolidated balance sheet Fair value
Derivative liabilities designated as hedges:
Interest rate swaps Other long-term liabilities $ 6.6
Total derivative liabilities $ 6.6
51