Electronic Arts 2001 Annual Report Download - page 33
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 33 of the 2001 Electronic Arts annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ELECTRONIC ARTS
31
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Market Risk
We are exposed to various market risks, including the changes in foreign currency exchange rates and
interest rates. Market risk is the potential loss arising from changes in market rates and prices. Foreign exchange
contracts used to hedge foreign currency exposures and short-term investments are subject to market risk. We do
not consider our cash and cash equivalents to be subject to interest rate risk due to their short maturities. We do
not enter into derivatives or other financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes.
FOREIGN CURRENCY EXCHANGE RATE RISK We utilize foreign exchange contracts to hedge foreign currency
exposures of underlying assets and liabilities, primarily certain intercompany receivables that are denominated in
foreign currencies, thereby, limiting our risk. Gains and losses on foreign exchange contracts are reflected in the
income statement. At March 31, 2001, we had foreign exchange contracts, all with maturities of less than nine
months to purchase and sell approximately $279,415,000 in foreign currencies, primarily British Pounds,
European Currency Units (“Euro”), Canadian Dollars, Japanese Yen and other currencies.
Fair value represents the difference in value of the contracts at the spot rate and the forward rate. The counter-
parties to these contracts are substantial and creditworthy multinational commercial banks. The risks of counter-
party nonperformance associated with these contracts are not considered to be material. Notwithstanding our
efforts to manage foreign exchange risks, there can be no assurances that our hedging activities will adequately
protect us against the risks associated with foreign currency fluctuations.
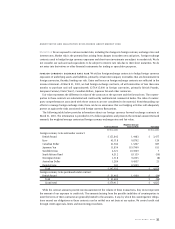
The following table below provides information about our foreign currency forward exchange contracts at
March 31, 2001. The information is provided in U.S. dollar equivalents and presents the notional amount (forward
amount), the weighted average contractual foreign currency exchange rates and fair value.
Weighted-Average
Contract Amount Contract Rate Fair Value
(In thousands) (In thousands)
Foreign currency to be sold under contract:
British Pound $ 155,842 1.4483 $ 3,477
Euro 45,718 0.8792 120
Canadian Dollar 21,942 1.5267 687
Japanese Yen 11,854 119.7900 611
Swedish Krona 4,521 10.3969 7
South African Rand 4,312 8.1159 (56)
Norwegian Krone 1,518 9.2235 (8)
Australian Dollar 1,284 0.4937 21
Danish Krone 941 8.5009 –
Total $ 247,932 $ 4,859
Foreign currency to be purchased under contract:
British Pound $ 31,483 1.4160 $ (34)
Total $ 31,483 $ (34)
Grand total $ 279,415 $ 4,825
While the contract amounts provide one measurement of the volume of these transactions, they do not represent
the amount of our exposure to credit risk. The amounts (arising from the possible inabilities of counterparties to
meet the terms of their contracts) are generally limited to the amounts, if any, by which the counterparties’ obliga-
tions exceed our obligations as these contracts can be settled on a net basis at our option. We control credit risk
through credit approvals, limits and monitoring procedures.