Microsoft 2005 Annual Report Download - page 38
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 38 of the 2005 Microsoft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
PAGE 37
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to foreign currency, interest rate, fixed income, equity and commodity price risks. A portion of these risks is
hedged, but fluctuations could impact our results of operations and financial position. We hedge a portion of anticipated
revenue and accounts receivable exposure to foreign currency fluctuations, primarily with option contracts. We monitor our
foreign currency exposures daily to maximize the overall effectiveness of our foreign currency hedge positions. Principal
currencies hedged include the euro, Japanese yen, British pound, and Canadian dollar. Fixed income securities are subject to
interest rate risk. The portfolio is diversified and structured to minimize credit risk. Securities held in our equity and other
investments portfolio are subject to price risk, and are generally not hedged. However, we use options to hedge our price risk on
certain equity securities that are held primarily for strategic purposes.
We use a value-at-risk (VAR) model to estimate and quantify our market risks. VAR is the expected loss, for a given
confidence level, in fair value of our portfolio due to adverse market movements over a defined time horizon. The VAR model is
not intended to represent actual losses in fair value, but is used as a risk estimation and management tool. The model used for
currencies and equities is geometric Brownian motion, which allows incorporation of optionality with regard to these risk
exposures. For interest rate risk, the mean reverting geometric Brownian motion is used to reflect the principle that fixed-income
securities prices revert to maturity value over time.
VAR is calculated by, first, simulating 10,000 market price paths over a specified period of time for equities, interest rates
and foreign exchange rates, taking into account historical correlations among the different rates and prices. Each resulting
unique set of equities prices, interest rates, and foreign exchange rates is then applied to substantially all individual holdings to
re-price each holding. The 250th worst performance (out of 10,000) represents the VAR over a specified period of time at the
97.5 percentile confidence level. Several risk factors are not captured in the model, including liquidity risk, operational risk,
credit risk, and legal risk.
Certain securities in our equity portfolio are held for strategic purposes. We hedge the value of a portion of these securities
through the use of derivative contracts such as put-call collars. In these arrangements, we hedge a security’s equity price risk
below the purchased put strike and forgo most or all of the benefits of the security’s appreciation above the sold call strike, in
exchange for the premium received for the sold call. We also hold equity securities for general investment return purposes. We
have incurred material impairment charges related to these securities in previous periods. The VAR amounts disclosed below
are used as a risk management tool and reflect an estimate of potential reductions in fair value of our portfolio. Losses in fair
value over the specified holding period can exceed the reported VAR by significant amounts and can also accumulate over a
longer time horizon than the specified holding period used in the VAR analysis. VAR amounts are not necessarily reflective of
potential accounting losses, including determinations of other-than-temporary losses in fair value in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
The VAR numbers are shown separately for interest rate, currency, equity and commodity risks. These VAR numbers include
the underlying portfolio positions and related hedges. We use historical data to estimate VAR. Given the reliance on historical
data, VAR is most effective in estimating risk exposures in markets in which there are no fundamental changes or shifts in
market conditions. An inherent limitation in VAR is that the distribution of past changes in market risk factors may not produce
accurate predictions of future market risk.
Management began using a 1-day VAR for internal risk measurement purposes effective for the quarter-ended March 31,
2005. The effect of changing from 20-day VAR to 1-day VAR was not material and there have been no modifications to the
assumptions or parameters within the model. The following table sets forth the 1-day VAR for substantially all of our positions.
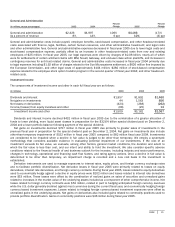
(In millions)
Y
ear ended June 30, 2005
Risk Categories
2004 2005 Average High Low
Interest rates
$ 67 $
88
$
68
$ 94
$
37
Currency
rates 46 52 36 55 12
Equity prices 173 164 166 187 141
Commodity
prices –14 6 14 –
The total 1-day VAR for the combined risk categories was $195 million at June 30, 2005 and $187 million at June 30, 2004.
The total VAR is 39% less at June 30, 2005 and 35% less at June, 30 2004 than the sum of the separate risk categories for
each of those years in the above table, due to the diversification benefit of the combination of risks.