Microsoft 2005 Annual Report Download - page 62
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 62 of the 2005 Microsoft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
PAGE 61
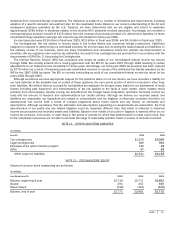
GAAP. The segments are designed to allocate resources internally and provide a framework to determine management
responsibility. Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise about which separate financial information is
available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker, or decision making group, in deciding how to allocate
resources and in assessing performance. Our chief operating decision maker is our Chief Executive Officer. The types of
products and services provided by each segment are summarized below:
Client – Windows XP Professional and Home, Media Center Edition, Tablet PC Edition, and other standard Windows operating
systems.
Server and Tools – Server software licenses and client access licenses (CALs) for Windows Server, Microsoft SQL Server,
Exchange Server, and other server products. Also includes developer tools, training, certification, Microsoft Press, Premier and
Professional product support services, and Microsoft Consulting Services.
Information Worker – Microsoft Office, Microsoft Project, Microsoft Visio, SharePoint Portal Server CALs, other information
worker products including Microsoft LiveMeeting and OneNote, an allocation for Server CALs, and professional product support
services.
Microsoft Business Solutions – Microsoft Great Plains, Microsoft Navision, Microsoft Axapta, Microsoft Solomon, Microsoft CRM,
Microsoft Retail Management System, Microsoft Point of Sale and other business applications and services including the
Microsoft Partner Program. Microsoft Business Solutions also develops Microsoft Office Small Business Accounting and
Business Contact Manager for Outlook, which are marketed by Information Worker.
MSN – Personal communication services, such as e-mail and instant messaging, and online information offerings, such as MSN
Search and the MSN portals and channels, and online paid services including MSN Internet Access, MSN Premium Web
Services, and MSN Mobile service.
Mobile and Embedded Devices – Windows Mobile software, Windows Embedded operating systems, MapPoint, and Windows
Automotive.
Home and Entertainment – Microsoft Xbox video game console system, PC games, mice, keyboards, Mac Office, and TV
platform products.
Because of our integrated business structure, operating costs included in one segment may benefit other segments, and
therefore these segments are not designed to measure operating income or loss directly related to the products included in
each segment. Inter-segment cost commissions are estimated by management and used to compensate or charge each
segment for such shared costs and to incent shared efforts. Management will continually evaluate the alignment of product
development organizations, sales organizations, and inter-segment commissions for segment reporting purposes, which may
result in changes to segment allocations in future periods.
Assets are not allocated to segments for internal reporting presentations. A portion of amortization and depreciation is
included with various other costs in an overhead allocation to each segment and it is impracticable for us to separately identify
the amount of amortization and depreciation by segment that is included in the measure of segment profit or loss.
Reconciling amounts include adjustments to conform with U.S. GAAP and corporate-level activity not specifically attributed to
a segment. Significant internal accounting policies that differ from U.S. GAAP relate to revenue recognition, income statement
classification, quarter end cut off timing, and accelerated amortization for depreciation, stock awards, and performance-based
stock awards. In addition, certain revenue and expenses are excluded from segments or included in corporate-level activity
including certain legal settlements and accruals for legal contingencies.