Microsoft 2005 Annual Report Download - page 45
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 45 of the 2005 Microsoft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (CONTINUED)
PAGE 44
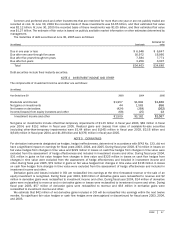
Foreign Currency Risk. Certain forecasted transactions and assets are exposed to foreign currency risk. We monitor our
foreign currency exposures daily to maximize the overall effectiveness of our foreign currency hedge positions. Options are used
to hedge a portion of forecasted international revenue for up to three years in the future and are designated as cash-flow
hedging instruments under Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments
and Hedging Activities. Principal currencies hedged include the euro, Japanese yen, British pound, and Canadian dollar. Certain
non-U.S. dollar denominated securities are hedged using foreign exchange forward contracts that are designated as fair-value
hedging instruments under SFAS No. 133. Certain options and forwards not designated as hedging instruments under SFAS No.
133 are also used to hedge the impact of the variability in exchange rates on accounts receivable and collections denominated
in certain foreign currencies and to manage other foreign currency exposures.
Equities Price Risk. Equity investments are subject to market price risk. From time to time, we use and designate options to
hedge fair values and cash flows on certain equity securities. We determine the security, or forecasted sale thereof, selected for
hedging by evaluating market conditions, up-front costs, and other relevant factors. Certain options, futures and swap contracts,
not designated as hedging instruments under SFAS No. 133, are also used to manage equity exposures.
Interest Rate Risk. Fixed-income securities are subject to interest rate risk. The fixed-income portfolio is diversified and
consists primarily of investment grade securities to minimize credit risk. We use exchange-traded option and future contracts
and over-the-counter swap contracts, not designated as hedging instruments under SFAS No. 133, to hedge interest rate risk.
Other Derivatives. Swap contracts, not designated as hedging instruments under SFAS No. 133, are used to manage
exposures to credit risks, enhance returns, and to facilitate portfolio diversification. In addition, we may invest in warrants to
purchase securities of other companies as a strategic investment. Warrants that can be net share settled are deemed derivative
financial instruments and are not designated as hedging instruments. To Be Announced (TBAs) forward purchase commitments
of mortgage-backed assets are also considered derivatives in cases where physical delivery of the assets are not taken at the
earliest available delivery date. All derivative instruments not designated as hedging instruments are recorded at fair value, with
changes in value recognized in earnings during the period of change.
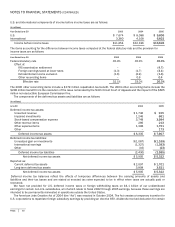
ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS
The allowance for doubtful accounts reflects our best estimate of probable losses inherent in the accounts receivable balance.
We determine the allowance based on known troubled accounts, historical experience, and other currently available evidence.
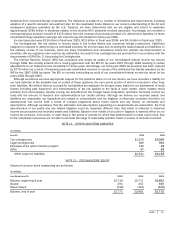
Activity in the allowance for doubtful accounts is as follows:
(In millions)
Y
ear Ended June 30 Balance at
beginning of period
Charged
t
o
costs
and expenses
Write-offs
and other
Balance
at
end of period
2003 $209
$118 $ (85) $242
2004 242
44 (120) 166
2005 166
48 (43) 171
INVENTORIES
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market, using the average cost method. Cost includes materials, labor, and
manufacturing overhead related to the purchase and production of inventories. We regularly review inventory quantities on
hand, future purchase commitments with our suppliers, and the estimated utility of our inventory. If our review indicates a
reduction in utility below carrying value, we reduce our inventory to a new cost basis.
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
Property and equipment is stated at cost and depreciated using the straight-line method over the shorter of the estimated life of
the asset or the lease term, ranging from one to 15 years. Computer software developed or obtained for internal use is
depreciated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the software, generally three years or less.
GOODWILL
Goodwill is tested for impairment on an annual basis as of July 1, and between annual tests if indicators of potential impairment
exist, using a fair-value-based approach. No impairment of goodwill has been identified during any of the periods presented.