Nike 2016 Annual Report Download - page 65
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 65 of the 2016 Nike annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
PART II
NOTE 15 — Commitments and Contingencies
The Company leases retail store space, certain distribution and warehouse facilities, and office space and other non-real estate assets under operating leases
expiring from 1 to 18 years after May 31, 2016. Rent expense was $661 million, $594 million and $533 million for the years ended May 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014,
respectively. Amounts of minimum future annual commitments under non-cancelable operating and capital leases are as follows (in millions):
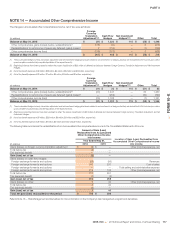
2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Thereafter Total
Operating leases $ 491 $ 453 $ 395 $ 347 $ 301 $ 1,244 $ 3,231
Capital leases $ 7 $ 5 $ 2 $ 1 $ — $ — $ 15
As of May 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had letters of credit outstanding
totaling $157 million and $165 million, respectively. These letters of credit
were generally issued for the purchase of inventory and guarantees of the
Company’s performance under certain self-insurance and other programs.
In connection with various contracts and agreements, the Company provides
routine indemnification relating to the enforceability of intellectual property
rights, coverage for legal issues that arise and other items where the
Company is acting as the guarantor. Currently, the Company has several
such agreements in place. However, based on the Company’s historical
experience and the estimated probability of future loss, the Company has
determined that the fair value of such indemnification is not material to the
Company’s financial position or results of operations.
In the ordinary course of its business, the Company is involved in various legal
proceedings involving contractual and employment relationships, product
liability claims, trademark rights and a variety of other matters. While the
Company cannot predict the outcome of its pending legal matters with
certainty, the Company does not believe any currently identified claim,
proceeding or litigation, either individually or in aggregate, will have a material
impact on the Company’s results of operations, financial position or cash
flows.
NOTE 16 — Risk Management and Derivatives
The Company is exposed to global market risks, including the effect of
changes in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates, and uses
derivatives to manage financial exposures that occur in the normal course of
business. The Company does not hold or issue derivatives for trading or
speculative purposes.
The Company may elect to designate certain derivatives as hedging
instruments under the accounting standards for derivatives and hedging. The
Company formally documents all relationships between designated hedging
instruments and hedged items as well as its risk management objectives and
strategies for undertaking hedge transactions. This process includes linking all
derivatives designated as hedges to either recognized assets or liabilities or
forecasted transactions.
The majority of derivatives outstanding as of May 31, 2016 are designated as
foreign currency cash flow hedges, primarily for Euro/U.S. Dollar, British
Pound/Euro and Japanese Yen/U.S. Dollar currency pairs. All derivatives are
recognized on the Consolidated Balance Sheets at fair value and classified
based on the instrument’s maturity date.
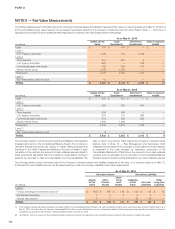
The following table presents the fair values of derivative instruments included within the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of May 31, 2016 and 2015:
Asset Derivatives Liability Derivatives
(In millions)
Balance Sheet
Location 2016 2015
Balance Sheet
Location 2016 2015
Derivatives formally designated
as hedging instruments:
Foreign exchange forwards
and options Prepaid expenses and
other current assets $ 447 $ 825 Accrued liabilities $ 38 $ 140
Interest rate swaps Prepaid expenses and
other current assets 7 78 Accrued liabilities 45 —
Foreign exchange forwards
and options Deferred income taxes
and other assets 90 520 Deferred income taxes
and other liabilities 12 4
Interest rate swaps Deferred income taxes
and other assets — — Deferred income taxes
and other liabilities — —
Total derivatives formally
designated as hedging
instruments 544 1,423 95 144
Derivatives not designated as
hedging instruments:
Foreign exchange forwards
and options Prepaid expenses and
other current assets 40 209 Accrued liabilities 76 20
Embedded derivatives Prepaid expenses and
other current assets 2 2 Accrued liabilities 2 2
Foreign exchange forwards
and options Deferred income taxes
and other assets 26 — Deferred income taxes
and other liabilities 19 —
Embedded derivatives Deferred income taxes
and other assets 5 5 Deferred income taxes
and other liabilities 7 9
Total derivatives not designated
as hedging instruments 73 216 104 31
TOTAL DERIVATIVES $ 617 $ 1,639 $ 199 $ 175
118