HSBC 2006 Annual Report Download - page 225
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 225 of the 2006 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327 -
 328
328 -
 329
329 -
 330
330 -
 331
331 -
 332
332 -
 333
333 -
 334
334 -
 335
335 -
 336
336 -
 337
337 -
 338
338 -
 339
339 -
 340
340 -
 341
341 -
 342
342 -
 343
343 -
 344
344 -
 345
345 -
 346
346 -
 347
347 -
 348
348 -
 349
349 -
 350
350 -
 351
351 -
 352
352 -
 353
353 -
 354
354 -
 355
355 -
 356
356 -
 357
357 -
 358
358 -
 359
359 -
 360
360 -
 361
361 -
 362
362 -
 363
363 -
 364
364 -
 365
365 -
 366
366 -
 367
367 -
 368
368 -
 369
369 -
 370
370 -
 371
371 -
 372
372 -
 373
373 -
 374
374 -
 375
375 -
 376
376 -
 377
377 -
 378
378 -
 379
379 -
 380
380 -
 381
381 -
 382
382 -
 383
383 -
 384
384 -
 385
385 -
 386
386 -
 387
387 -
 388
388 -
 389
389 -
 390
390 -
 391
391 -
 392
392 -
 393
393 -
 394
394 -
 395
395 -
 396
396 -
 397
397 -
 398
398 -
 399
399 -
 400
400 -
 401
401 -
 402
402 -
 403
403 -
 404
404 -
 405
405 -
 406
406 -
 407
407 -
 408
408 -
 409
409 -
 410
410 -
 411
411 -
 412
412 -
 413
413 -
 414
414 -
 415
415 -
 416
416 -
 417
417 -
 418
418 -
 419
419 -
 420
420 -
 421
421 -
 422
422 -
 423
423 -
 424
424 -
 425
425 -
 426
426 -
 427
427 -
 428
428 -
 429
429 -
 430
430 -
 431
431 -
 432
432 -
 433
433 -
 434
434 -
 435
435 -
 436
436 -
 437
437 -
 438
438 -
 439
439 -
 440
440 -
 441
441 -
 442
442 -
 443
443 -
 444
444 -
 445
445 -
 446
446 -
 447
447 -
 448
448 -
 449
449 -
 450
450 -
 451
451 -
 452
452 -
 453
453 -
 454
454 -
 455
455 -
 456
456 -
 457
457 -
 458
458
 |
 |
223
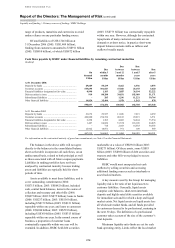
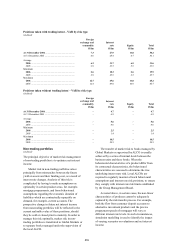
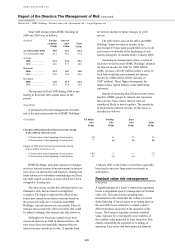
The sensitivities are illustrative only and are
based on simplified scenarios. The table shows
interest rate risk exposures arising in available-for-
sale portfolios and from cash flow hedges which
are marked-to-market through reserves. These
particular exposures form only a part of the
Group’s overall interest rate exposures. The
accounting treatment under IFRSs of the Group’s
remaining interest rate exposures, while
economically largely offsetting the exposures
shown in the above table, does not require
revaluation movements to go to reserves.
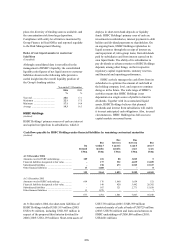
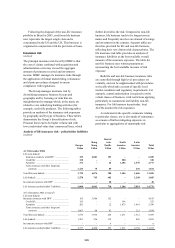
Structural foreign exchange exposures
(Unaudited)
Structural foreign exchange exposures represent net
investments in subsidiaries, branches or associated
undertakings, the functional currencies of which
are currencies other than the US dollar.
Exchange differences on structural exposures
are recorded in the consolidated statement of
recognised income and expense. The main
operating (or functional) currencies in which
HSBC’s business is transacted are the US dollar,
the Hong Kong dollar, sterling, the euro, the
Mexican peso, the Brazilian real and the Chinese
renminbi. As the US dollar and currencies linked to
it form the dominant currency bloc in which
HSBC’s operations transact business, HSBC
Holdings prepares its consolidated financial
statements in US dollars. HSBC’s consolidated
balance sheet is, therefore, affected by exchange
differences between the US dollar and all the non-
US dollar functional currencies of underlying
subsidiaries.
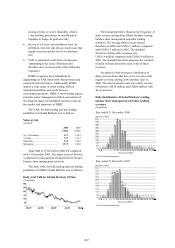
HSBC hedges structural foreign exchange
exposures only in limited circumstances. HSBC’s
structural foreign exchange exposures are managed
with the primary objective of ensuring, where
practical, that HSBC’s consolidated capital ratios,
and the capital ratios of individual banking
subsidiaries, are protected from the effect of
changes in exchange rates. This is usually achieved
by ensuring that, for each subsidiary bank, the ratio
of structural exposures in a given currency to risk-
weighted assets denominated in that currency is
broadly equal to the capital ratio of the subsidiary
in question.
Selective hedges were in place during 2006.
Hedging is undertaken using forward foreign
exchange contracts which are accounted for under
IFRSs as hedges of a net investment in a foreign
operation, or by financing with borrowings in the
same currencies as the functional currencies
involved. There was no ineffectiveness arising from
these hedges in the year ended 31 December 2006.
There was no material effect from exchange
differences on HSBC’s capital ratios during the
year.
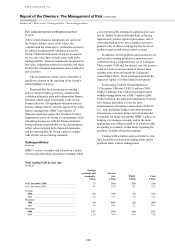
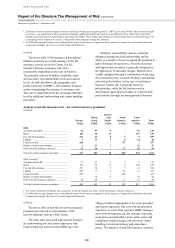
HSBC Holdings
(Audited)
As a financial services holding company, HSBC
Holdings has limited market risk activity. Its
activities predominantly involve maintaining
sufficient capital resources to support the Group’s
diverse activities; allocating these capital resources
across the Group’s businesses; earning dividend
and interest income on its investments in the
Group’s businesses; providing dividend payments
to HSBC Holdings’ equity shareholders and interest
payments to providers of debt capital; and
maintaining a supply of short-term cash resources.
It does not take proprietary trading positions.
The objectives of HSBC Holdings’ market risk
management are to minimise income statement
volatility arising from short-term cash balances and
funding positions; to minimise the market risk
arising from long-term investments and long-term
liabilities; and to protect distributable reserves from
any adverse market risk variables.
Market risk for HSBC Holdings is monitored
by its Structural Positions Review Group.
The main market risks to which HSBC
Holdings is exposed are interest rate risk and
foreign currency risk.
HSBC Holdings is exposed to interest rate risk
on debt capital investments in, and loans to,
subsidiary undertakings; on debt capital issues; and
on short-term cash resources.
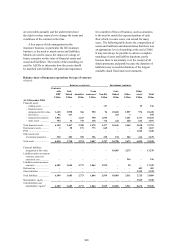
Certain loans to subsidiary undertakings of a
capital nature that are not denominated in the
functional currency of either the provider or the
recipient are accounted for as financial assets.
Changes in the carrying amount of these assets due
to exchange differences are taken directly to the
income statement. These loans, and the associated
foreign exchange exposures, are eliminated on a
Group consolidated basis.
Revaluations due to foreign exchange rate
movements affecting loans to subsidiary
undertakings of a capital nature which are
denominated in the functional currency of either
the borrower or the recipient, are taken directly to
reserves. Equity investments in subsidiary
undertakings are accounted for on a cost basis and
are not revalued following movements in exchange
rates.
