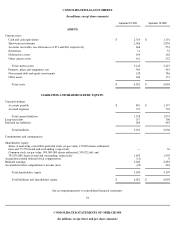
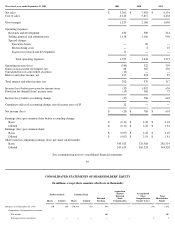
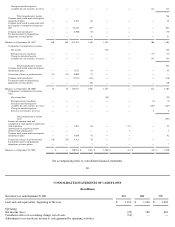
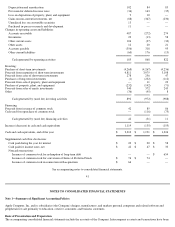
Apple 2001 Annual Report Download - page 23
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 23 of the 2001 Apple annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
The Company's retail initiative requires a substantial investment and commitment of resources and is subject to numerous risks and
uncertainties.
Since May of 2001, the Company has opened 27 retail stores in the United States and anticipates opening more stores in calendar 2002. The
Company's retail initiative has required substantial investment in equipment and leasehold improvements, information systems, inventory, and
personnel. The Company has also entered into substantial operating leases commitments for retail space with lease terms ranging from 5 to
12 years. The Company would incur substantial costs should it choose to terminate this initiative or close individual stores. Such costs could
adversely affect the company's results of operations and financial condition.
Despite the Company's current plan for its Retail segment to experience only a small loss during 2002, many of the general risks and
uncertainties the Company faces could also have an adverse impact on the Retail segment. Also, many factors unique to retail operations
present risks and uncertainties, some of which are beyond the Company's control, that could adversely affect the Retail segment's future results,
cause its actual results to differ from those currently expected, and/or have an adverse effect on the Company's consolidated results of
operations. Potential risks and uncertainties unique to retail operations that could have an adverse impact on the Retail segment include, among
other things, macro-economic factors that have a negative impact on general retail activity; inability to manage costs associated with store
construction and operation; lack of consumer acceptance of the Company's retail approach; failure to attract new users to the Macintosh
platform; inability to sell third-party hardware and software products at
28
adequate margins; failure to manage relationships with existing retail channel partners; lack of experience in managing retail operations; costs
associated with unanticipated fluctuations in the value of Apple-branded and third-party retail inventory; and inability to obtain quality retail
locations at reasonable cost.
The Company faces increasing competition in the U.S. education market.
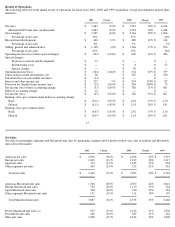
Sales in the United States to both elementary and secondary schools, as well as for college and university customers, remains a core market for
Apple, combined accounting for over 26% of net sales in 2001. Several competitors of the Company have either targeted or announced their
intention to target the education market for personal computers. As a result, the Company's overall share of this market has declined. Although
the Company has initiated a plan to strengthen its position in the education market and did experience some success in stabilizing its position in
this critical market during 2001, there can be no assurance that the Company will be able to increase its share of the education market or
maintain its existing share of that market. Failure to increase or maintain market share in the education market may have an adverse impact on
the Company's operating results and financial condition.
In November 2001, Microsoft Corporation reached a tentative settlement to resolve more than 100 private antitrust class-action lawsuits. The
proposed settlement requires that Microsoft donate cash, Microsoft software, refurbished computers, and services, valued by Microsoft at
approximately $1 billion, to more than 10,000 public schools in the United States over the next five years. The terms of this proposed
settlement may place additional pressure on the Company's ability to maintain or grow its existing share in the U.S. education market and could
have an adverse impact on the Company's operating results and financial condition.
The Company's future operating performance is dependent on the performance of distributors and other resellers of the Company's products.
The Company distributes its products through wholesalers, resellers, national and regional retailers and cataloguers. In addition, the Company
also sells many of its products and resells certain third-party products in most of its major markets directly to end users, certain education
customers, and certain resellers through its online stores around the world. The Company also sells its own products and certain third-party
products through its retail stores in the United States. Many of the Company's significant resellers operate on narrow product margins, and may
distribute products from competing manufacturers. Considerable trade receivables that are not covered by collateral or credit insurance are
outstanding with the Company's distribution and retail channel partners. The Company's business and financial results could be adversely
affected if the financial condition of these resellers weakened, if resellers within consumer channels were to cease distribution of the
Company's products, or if uncertainty regarding demand for the Company's products caused resellers to reduce their ordering and marketing of
the Company's products.
Further information regarding risks associated with Marketing and Distribution may be found in Part I, Item 1 of this Form 10-K under the
heading "Markets and Distribution," which information is hereby incorporated by reference.
The Company's business is subject to the risks of international operations.
A large portion of the Company's revenue is derived from its international operations. As a result, the Company's operating results and
financial condition could be significantly affected by risks associated with international activities, including economic and labor conditions,
political instability, tax laws (including U.S. taxes on foreign subsidiaries), and changes in the value of the U.S. dollar versus the local currency
in which the products are sold and goods and services are purchased. Historically, the Company's primary exposure to movements in foreign
currency exchange rates relate to non-dollar denominated sales in Europe, Japan, Australia, Canada, and certain parts of Asia and non-dollar
denominated operating expenses incurred throughout the world. Weaknesses in foreign currencies, particularly the Japanese Yen and the Euro,
can adversely impact consumer demand for the Company's products and the U.S. dollar
29