Apple 2001 Annual Report Download - page 36
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 36 of the 2001 Apple annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
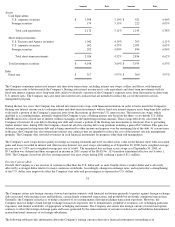
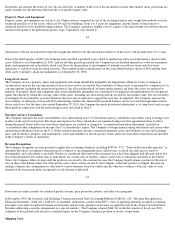
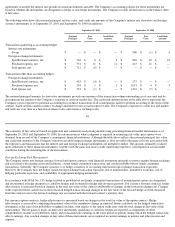
The Company's shipping and handling costs are included in cost of sales for all periods presented.
Warranty Expense
The Company provides currently for the estimated cost that may be incurred under product warranties at the time related revenue is recognized.
Research and Development
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Development costs of computer software to be sold, leased or otherwise marketed
are subject to capitalization beginning when a product's technological feasibility has been established and ending when a product is available
for general release to customers. In almost all instances, the Company's products are released soon after technological feasibility has been
established. Therefore, costs subsequent to achieving technological feasibility have not been significant, and historically all software
development costs have been expensed. However, during 2001 the Company incurred substantial development costs associated with
completion of Mac OS X, its new Macintosh operating system, subsequent to release of a public beta version of the product and prior to release
of the final product version. As a result, the Company capitalized approximately $5.4 million of development costs during 2001 associated with
final development of Mac OS X. Related amortization is computed by use of the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the asset
of 8 years and resulted in amortization expense of approximately $350,000 in 2001.
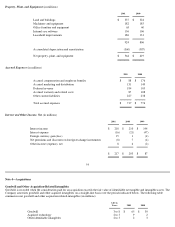
Advertising Costs
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred. Advertising expense was $261 million, $281 million, and $208 million for 2001, 2000, and 1999,
respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company measures compensation expense for its employee stock-based compensation plans using the intrinsic value method and has
provided pro forma disclosures of the effect on net income and earnings per share as if the fair value-based method had been applied in
measuring compensation expense.
Earnings Per Common Share
Basic earnings per common share is computed by dividing income available to common shareholders by the weighted-average number of
shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per common share is computed by dividing income available to
common shareholders by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period increased to include the
number of additional shares of common stock that would have been outstanding if the dilutive potential shares of
45
common stock had been issued. The dilutive effect of outstanding options is reflected in diluted earnings per share by application of the
treasury stock method. The dilutive effect of convertible securities is reflected using the if-converted method. Dilutive potential shares of
common stock related to stock options were excluded from the calculation of diluted loss per common share for 2001 because their effect
would have been antidilutive.
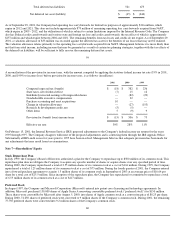
Stock Split
On June 21, 2000, the Company effected a two-for-one stock split in the form of a Common Stock dividend to shareholders of record as of
May 19, 2000. All per share data and numbers of Common shares have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the stock split.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income consists of two components, net income and other comprehensive income. Other comprehensive income refers to
revenue, expenses, gains and losses that under generally accepted accounting principles are recorded as an element of shareholders' equity but
are excluded from net income. The Company's other comprehensive income is comprised of foreign currency translation adjustments from
those subsidiaries not using the U.S. dollar as their functional currency, from unrealized gains and losses on marketable securities categorized
as available-for-sale, and from net deferred gains and losses on certain derivative instruments accounted for as cash flow hedges.
Segment Information
The Company reports segment information based on the "management" approach. The management approach designates the internal reporting
used by management for making decisions and assessing performance as the source of the Company's reportable segments. Information about
the Company's products, major customers, and geographic areas on a company-wide basis is also disclosed.
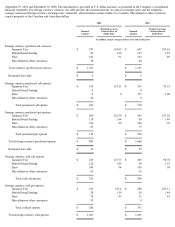
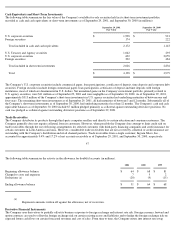
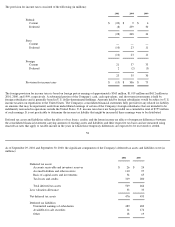
Note 2—Financial Instruments
The carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and accrued liabilities approximate their fair value
due to the short maturities of those instruments.
46