McDonalds 2009 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 37 of the 2009 McDonalds annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
cash flows. The Company adopted the disclosure requirements
as of January 1, 2009 on a prospective basis; accordingly, dis-
closures related to income and other comprehensive income
(OCI) for prior periods have not been presented. The adoption
had no impact on our consolidated financial statements, besides
the additional disclosures.
The Company is exposed to global market risks, including the
effect of changes in interest rates and foreign currency fluctua-
tions. The Company uses foreign currency denominated debt and
derivative instruments to mitigate the impact of these changes.
The Company does not use derivatives with a level of complexity
or with a risk higher than the exposures to be hedged and does
not hold or issue derivatives for trading purposes.
The Company formally documents all relationships between
hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as its risk man-
agement objective and strategy for undertaking hedging
transactions. The Company’s derivatives that are designated as
hedging instruments consist mainly of interest rate exchange
agreements, forward foreign currency exchange agreements and
foreign currency options. Interest rate exchange agreements are
entered into to manage the interest rate risk associated with the
Company’s fixed and floating-rate borrowings. Forward foreign
currency exchange agreements and foreign currency options are
entered into to mitigate the risk that forecasted foreign currency
cash flows (such as royalties denominated in foreign currencies)
will be adversely affected by changes in foreign currency
exchange rates. Certain foreign currency denominated debt is
used, in part, to protect the value of the Company’s investments
in certain foreign subsidiaries and affiliates from changes in for-
eign currency exchange rates.
The Company also enters into certain derivatives that are not
designated as hedging instruments. The Company has entered
into derivative contracts to hedge market-driven changes in cer-
tain of its supplemental benefit plan liabilities. Changes in the fair
value of these derivatives are recorded in selling, general &
administrative expenses. In addition, the Company uses forward
foreign currency exchange agreements and foreign currency
exchange agreements to mitigate the change in fair value of
certain foreign denominated assets and liabilities. Since these
derivatives are not designated as hedging instruments, the
changes in the fair value of these hedges are recognized
immediately in nonoperating (income) expense together with the
translation gain or loss from the hedged balance sheet position.
A portion of the Company’s foreign currency options (more fully
described in the Cash Flow Hedging Strategy section) are
undesignated as hedging instruments as the underlying foreign
currency royalties are earned.
All derivative instruments designated as hedging instruments
are classified as fair value, cash flow or net investment hedges.
All derivatives (including those not designated as hedging
instruments) are recognized on the Consolidated balance sheet
at fair value and classified based on the instruments’ maturity
date. Changes in the fair value measurements of the derivative
instruments are reflected as adjustments to OCI and/or current
earnings.
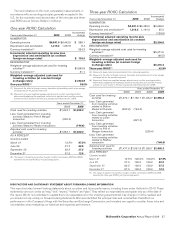
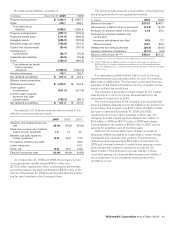
The following table presents the fair values of derivative instruments included on the Consolidated balance sheet:
Asset derivatives Liability derivatives
In millions
Balance sheet
classification 2009 2008
Balance sheet
classification 2009 2008
Derivatives designated as
hedging instruments
Foreign currency options Prepaid expenses and other
current assets $ 13.2 $ 43.8 Accrued payroll and other
liabilities $—
Interest rate exchange
agreements Prepaid expenses and other
current assets 1.4
Accrued payroll and other
liabilities
Forward foreign currency
exchange agreements Prepaid expenses and other
current assets 0.3
Accrued payroll and other
liabilities (0.1) $ (2.1)
Foreign currency options Miscellaneous other assets 5.4 5.0 Other long-term liabilities
Interest rate exchange
agreements Miscellaneous other assets 67.3 82.6 Other long-term liabilities (3.4) (3.5)
Total derivatives designated as
hedging instruments $ 87.6 $131.4 $(3.5) $ (5.6)
Derivatives not designated as
hedging instruments
Forward foreign currency
exchange agreements Prepaid expenses and other
current assets $ 9.3
Accrued payroll and other
liabilities $(5.4) $(20.0)
Derivatives hedging
supplemental benefit plan
liabilities Miscellaneous other assets 79.6 $ 90.2 Other long-term liabilities
Foreign currency exchange
agreements Miscellaneous other assets Other long-term liabilities (0.5)
Total derivatives not designated
as hedging instruments $ 88.9 $ 90.2 $(5.9) $(20.0)
Total derivatives(1) $176.5 $221.6 $(9.4) $(25.6)
(1) The fair value of derivatives is presented on a gross basis. Accordingly, the 2009 total asset and liability fair values do not agree with the values provided in the Fair Value Measurements
note, because that disclosure reflects netting adjustments of $2.4 million.
McDonald’s Corporation Annual Report 2009 35