McDonalds 2009 Annual Report Download - page 38
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 38 of the 2009 McDonalds annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
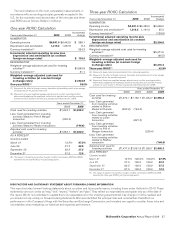
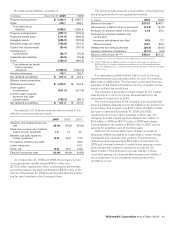
The following table presents the pretax amounts affecting income and other comprehensive income for the year ended December 31,
2009:
In millions
Derivatives in
Fair Value
Hedging Relationships
(Gain) Loss
Recognized in Income
on Derivative
Hedged Items in
Fair Value
Hedge Relationships
(Gain) Loss
Recognized in Income on
Related Hedged Items
Interest rate exchange
agreements $ 17.3 Fixed-rate debt $(17.3)
Derivatives in
Cash Flow
Hedging Relationships
(Gain) Loss
Recognized in Accumulated
OCI on Derivative
(Effective Portion)
(Gain) Loss
Reclassified from
Accumulated OCI into
Income (Effective Portion)
(Gain) Loss
Recognized in Income on
Derivative (Amount
Excluded from
Effectiveness Testing
and Ineffective Portion)
Foreign currency options $ 2.0 $(42.8) $ 27.0
Interest rate exchange
agreements(1) (2.1) (2.1)
Forward foreign currency
exchange agreements 1.4 (5.5) —
Total $ 1.3 $(50.4) $ 27.0
Derivatives in
Net Investment
Hedging Relationships
(Gain) Loss
Recognized in Accumulated
OCI on Derivative
(Effective Portion)
Foreign currency denominated
debt $ 51.3
Derivatives Not
Designated as
Hedging Instruments
(Gain) Loss
Recognized in Income
on Derivative
Forward foreign currency
exchange agreements $(12.4)
Derivatives hedging
supplemental benefit plan
liabilities(2) (2.4)
Foreign currency options (0.3)
Foreign currency exchange
agreements 0.5
Total $(14.6)
(Gains) losses recognized in income on derivatives are recorded in nonoperating (income) expense unless otherwise noted.
(1) The amount of (gain) loss reclassified from accumulated OCI into income is recorded in interest expense.
(2) The amount of (gain) loss recognized in income on the derivatives used to hedge the supplemental benefit plan liabilities is recorded in selling, general & administrative expenses.
• Fair value hedging strategy
The Company enters into fair value hedges to reduce the
exposure to changes in the fair values of certain liabilities. The fair
value hedges the Company enters into consist of interest rate
exchange agreements which convert a portion of its fixed-rate
debt into floating-rate debt. All of the Company’s interest rate
exchange agreements meet the shortcut method requirements.
Accordingly, changes in the fair values of the interest rate
exchange agreements are exactly offset by changes in the fair
value of the underlying debt. No ineffectiveness has been
recorded to net income related to interest rate exchange agree-
ments designated as fair value hedges for the year ended
December 31, 2009. A total of $2.1 billion of the Company’s out-
standing fixed-rate debt was effectively converted to floating-rate
debt resulting from the use of interest rate exchange agreements.
• Cash flow hedging strategy
The Company enters into cash flow hedges to reduce the
exposure to variability in certain expected future cash flows. The
types of cash flow hedges the Company enters into include
interest rate exchange agreements, forward foreign currency
exchange agreements and foreign currency options.
The Company periodically uses interest rate exchange agree-
ments to effectively convert a portion of floating-rate debt into
fixed-rate debt, and the agreements are designed to reduce the
impact of interest rate changes on future interest expense. At
December 31, 2009, none of the Company’s outstanding
floating-rate debt was effectively converted to fixed-rate debt
resulting from the use of interest rate exchange agreements.
To protect against the reduction in value of forecasted foreign
currency cash flows (such as royalties denominated in foreign
36 McDonald’s Corporation Annual Report 2009