Proctor and Gamble 2010 Annual Report Download - page 51
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 51 of the 2010 Proctor and Gamble annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
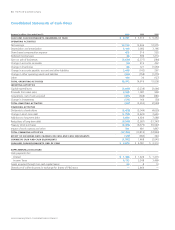
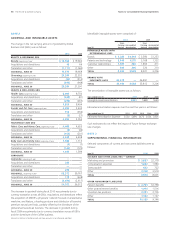
Management’s Discussion and Analysis The Procter & Gamble Company 49
Derivative positions can be monitored using techniques including
market valuation, sensitivity analysis and value-at-risk modeling. The
tests for interest rate, currency rate and commodity derivative positions
discussed below are based on the CorporateManager™ value-at-risk
model using a one-year horizon and a 95% confidence level. The
model incorporates the impact of correlation (the degree to which
exposures move together over time) and diversification (from holding
multiple currency, commodity and interest rate instruments) and
assumes that financial returns are normally distributed. Estimates of
volatility and correlations of market factors are drawn from the
RiskMetrics™ dataset as of June30, 2010. In cases where data is
unavailable in RiskMetrics™, a reasonable proxy is included.
Our market risk exposures relative to interest rates, currency rates and
commodity prices, as discussed below, have not changed materially
versus the previous reporting period. In addition, we are not aware
of any facts or circumstances that would significantly impact such
exposures in the near term.
Interest Rate Exposure on Financial Instruments. Interest rate swaps
are used to hedge exposures to interest rate movement on underlying
debt obligations. Certain interest rate swaps denominated in foreign
currencies are designated to hedge exposures to currency exchange rate
movements on our investments in foreign operations. These currency
interest rate swaps are designated as hedges of the Company’s foreign
net investments.
Based on our overall interest rate exposure as of and during the year
ended June30, 2010, including derivative and other instruments
sensitive to interest rates, we believe a near-term change in interest
rates, at a 95% confidence level based on historical interest rate
movements, would not materially affect our financial statements.
Currency Rate Exposure on Financial Instruments. Because we
manufacture and sell products and finance operations in a number of
countries throughout the world, we are exposed to the impact on
revenue and expenses of movements in currency exchange rates. The
primary purpose of our currency hedging activities is to reduce the
risk that our financial position will be adversely affected by short-term
changes in exchange rates. Corporate policy prescribes the range of
allowable hedging activity. We primarily use forward contracts with
maturities of less than 18 months. In addition, we enter into certain
currency swaps with maturities of up to five years to hedge our exposure
to exchange rate movements on intercompany financing transactions.
Based on our overall currency rate exposure as of and during the year
ended June30, 2010, we believe, at a 95% confidence level based
on historical currency rate movements, the impact of a near-term
change in currency rates on derivative and other instruments would
not materially affect our financial statements.
Commodity Price Exposure on Financial Instruments. We use raw
materials that are subject to price volatility caused by weather, supply
conditions, political and economic variables and other unpredictable
factors. In addition to fixed price contracts, we may use futures,
options and swap contracts to manage the volatility related to the
above exposures.
Based on our overall commodity price exposure as of and during the
year ended June30, 2010, we believe, at a 95% confidence level based
on historical commodity price movements, the impact of a near-term
change in commodity prices on derivative and other instruments
would not materially affect our financial statements.
Measures Not Defined By U.S. GAAP
Our discussion of financial results includes several “non-GAAP” finan-
cial measures. We believe these measures provide our investors with
additional information about our underlying results and trends, as
well as insight to some of the metrics used to evaluate management.
When used in MD&A, we have provided the comparable GAAP
measure in the discussion. These measures include:
Organic Sales Growth. Organic sales growth measures sales growth
excluding the impacts of foreign exchange, acquisitions and divestitures
from year-over-year comparisons. We believe this provides investors
with a more complete understanding of underlying results and trends
by providing sales growth on a consistent basis.
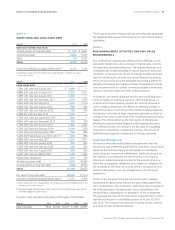
The following tables provide a numerical reconciliation of organic
sales growth to reported net sales growth:
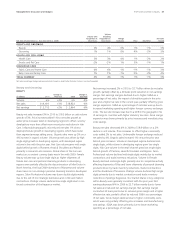
Year ended June 30, 2010
Net Sales
Growth
Foreign
Exchange
Impact
Acquisition/
Divestiture
Impact*
Organic
Sales
Growth
Beauty 3% 0% 0% 3%
Grooming 3% 0% 0% 3%
Health Care 2% 0% 0% 2%
Snacks and Pet Care 1% -1% 0% 0%
Fabric Care and Home Care 3% 1% 0% 4%
Baby Care and Family Care 4% 1% 0% 5%
TOTAL P&G 3% 1% -1% 3%
Year ended June 30, 2009
Net Sales
Growth
Foreign
Exchange
Impact
Acquisition/
Divestiture
Impact*
Organic
Sales
Growth
Beauty -4% 4% 1% 1%
Grooming -9% 6% 1% -2%
Health Care -7% 5% 1% -1%
Snacks and Pet Care -3% 4% 0% 1%
Fabric Care and Home Care -2% 5% 0% 3%
Baby Care and Family Care 1% 4% 2% 7%
TOTAL P&G -3% 4% 1% 2%
* Acquisition/Divestiture Impact includes rounding impacts necessary to reconcile net sales to
organic sales.