Target 2007 Annual Report Download - page 46
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 46 of the 2007 Target annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1. Summary of Accounting Policies
Organization Target Corporation (the Corporation or Target) operates large-format general merchandise and
food discount stores in the United States and a fully integrated online business, Target.com. Our credit card
operations represent an integral component of our core retail business, strengthening the bond with our
guests, driving incremental sales and contributing meaningfully to earnings. We operate as a single business
segment.
Consolidation The consolidated financial statements include the balances of the Corporation and its
subsidiaries after elimination of intercompany balances and transactions. All material subsidiaries are wholly
owned.
Use of estimates The preparation of our consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. Generally
Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) requires management to make estimates and assumptions affecting
reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual results may differ
significantly from those estimates.
Fiscal year Our fiscal year ends on the Saturday nearest January 31. Unless otherwise stated, references to
years in this report relate to fiscal years, rather than to calendar years. Fiscal year 2007 (2007) ended
February 2, 2008 and consisted of 52 weeks. Fiscal year 2006 (2006) ended February 3, 2007 and consisted of
53 weeks. Fiscal year 2005 (2005) ended January 28, 2006 and consisted of 52 weeks.
Reclassifications Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year
presentation.
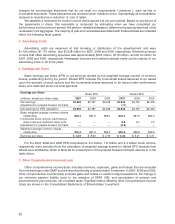
Share-based compensation We estimate the fair value of all share-based awards on the date of grant, which
we define as the date the award is approved by our Board of Directors or, for a limited number of awards to
team members who are not executive officers, the date the award is approved by management with
appropriate delegated authority. The majority of granted awards are nonqualified stock options that vest
annually in equal amounts over a four-year period, and all stock options have an exercise price equal to the fair
market value of our common stock on the date of grant. Generally, we recognize compensation expense for
awards on a straight-line basis over the four-year vesting period. In certain circumstances under our share-
based compensation plans, we allow for the vesting of team member awards to continue post-employment.
For such awards granted subsequent to our adoption of SFAS 123(R) and to the extent the team member
meets certain age and service requirements on the date of grant, we accelerate expense recognition such that
the value of the award is fully expensed over the team member’s minimum service period instead of over the
explicit vesting period. Awards granted prior to the adoption of SFAS 123(R) continue to be expensed over the
explicit vesting period. Additional information related to share-based awards is included in Note 25.
Derivative financial instruments Derivative financial instruments are carried at fair value on the balance
sheet. Our derivative instruments are primarily interest rate swaps that hedge the fair value of certain debt by
effectively converting interest from a fixed rate to a floating rate. These instruments qualify for hedge
accounting, and the associated assets and liabilities are recorded in the Consolidated Statements of Financial
Position. The changes in market value of an interest rate swap, as well as the offsetting change in market value
of the hedged debt, are recognized within earnings in the current period. Ineffectiveness would result when
changes in the market value of the hedged debt are not completely offset by changes in the market value of
the interest rate swap. There was no ineffectiveness recognized in 2007, 2006 or 2005 related to these
instruments. Further information related to interest rate swaps is included in Note 20 and Note 29.
From time to time, we enter into other interest rate derivative financial instruments, including interest rate
locks and interest rate forward contracts. Interest rate locks are used periodically as hedges of the interest rate
risk associated with the anticipated issuance of fixed-rate debt and are typically designated as hedges of
forecasted transactions. Interest rate forward contracts are used to offset a portion of our exposure to our
workers’ compensation and general liability obligations, which are recorded on a discounted basis, and these
instruments are not designated as accounting hedges.
28