American Express 2013 Annual Report Download - page 89
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 89 of the 2013 American Express annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
AMERICAN EXPRESS COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 11
OTHER LIABILITIES
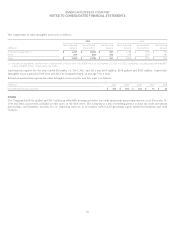
The following is a summary of other liabilities as of December 31:
(Millions) 2013 2012
Membership Rewards liability $ 6,151 $ 5,832
Employee-related liabilities(a) 2,227 2,224
Rebate and reward accruals(b) 2,210 2,079
Deferred card and other fees, net 1,314 1,286
Book overdraft balances 442 532
Other(c) 4,566 5,604
Total $ 16,910 $ 17,557
(a) Employee-related liabilities include employee benefit plan obligations and
incentive compensation.
(b) Rebate and reward accruals include payments to third-party card-issuing
partners and cash-back reward costs.
(c) Other includes accruals for general operating expenses, client incentives,
advertising and promotion, restructuring and reengineering reserves and
derivatives.
MEMBERSHIP REWARDS
The Membership Rewards program allows enrolled Card Members to
earn points that can be redeemed for a broad range of rewards
including travel, entertainment, retail certificates and merchandise.
The Company records a balance sheet liability that represents
management’s best estimate of the cost of points earned that are
expected to be redeemed. An ultimate redemption rate and weighted
average cost per point are key factors used to approximate
Membership Rewards liability. Management uses statistical and
actuarial models to estimate ultimate redemption rates based on
redemption trends, current enrollee redemption behavior, card
product type, enrollment tenure, card spend levels and credit
attributes. The weighted-average cost per point is determined using
actual redemptions during the previous 12 months, adjusted as
appropriate for certain changes in redemption costs that are not
representative of future cost expectations.
The expense for Membership Rewards points is included in
marketing, promotion, rewards and Card Member services expenses.
The Company periodically evaluates its liability estimation process
and assumptions based on developments in redemption patterns, cost
per point redeemed, partner contract changes and other factors.
DEFERRED CARD AND OTHER FEES, NET
The carrying amount of deferred card and other fees, net of deferred
direct acquisition costs and reserves for membership cancellations as
of December 31 was as follows:
(Millions) 2013 2012
Deferred card and other fees(a) $ 1,609 $ 1,566
Deferred direct acquisition costs (164) (154)
Reserves for membership cancellations (131) (126)
Deferred card and other fees, net $ 1,314 $ 1,286
(a) Includes deferred fees for Membership Rewards program participants.
NOTE 12
DERIVATIVES AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES
The Company uses derivative financial instruments (derivatives) to
manage exposures to various market risks. Derivatives derive their
value from an underlying variable or multiple variables, including
interest rate, foreign exchange, and equity index or price. These
instruments enable end users to increase, reduce or alter exposure to
various market risks and, for that reason, are an integral component of
the Company’s market risk management. The Company does not
engage in derivatives for trading purposes.
Market risk is the risk to earnings or value resulting from
movements in market prices. The Company’s market risk exposure is
primarily generated by:
폷Interest rate risk in its card, insurance and Travelers Cheque and
other prepaid products businesses, as well as its investment
portfolios; and
폷Foreign exchange risk in its operations outside the U.S. and the
associated funding of such operations.
The Company centrally monitors market risks using market risk limits
and escalation triggers as defined in its Asset/Liability Management
Policy.
The Company’s market exposures are in large part byproducts of
the delivery of its products and services. Interest rate risk arises
through the funding of Card Member receivables and fixed-rate loans
with variable-rate borrowings as well as through the risk to net
interest margin from changes in the relationship between benchmark
rates such as Prime and LIBOR.
Interest rate exposure within the Company’s charge card and fixed-
rate lending products is managed by varying the proportion of total
funding provided by short-term and variable-rate debt and deposits
compared to fixed-rate debt and deposits. In addition, interest rate
swaps are used from time to time to economically convert fixed-rate
debt obligations to variable-rate obligations or to convert variable-rate
debt obligations to fixed-rate obligations. The Company may change
the mix between variable-rate and fixed-rate funding based on changes
in business volumes and mix, among other factors.
Foreign exchange risk is generated by Card Member cross-
currency charges, foreign currency balance sheet exposures, foreign
subsidiary equity and foreign currency earnings in entities outside the
U.S. The Company’s foreign exchange risk is managed primarily by
entering into agreements to buy and sell currencies on a spot basis or
by hedging this market exposure to the extent it is economically
justified through various means, including the use of derivatives such
as foreign exchange forwards and cross-currency swap contracts,
which can help mitigate the Company’s exposure to specific
currencies.
In addition to the exposures identified above, effective August 1,
2011, the Company entered into a total return contract (TRC) to hedge
its exposure to changes in the fair value of its equity investment in ICBC
in local currency. Under the terms of the TRC, the Company receives
from the TRC counterparty an amount equivalent to any reduction in
the fair value of its investment in ICBC in local currency, and the
Company pays to the TRC counterparty an amount equivalent to any
increase in the fair value of its investment in local currency, along with
87