McDonalds 2015 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 39 of the 2015 McDonalds annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
McDonald's Corporation 2015 Annual Report 37
FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The Company measures certain financial assets and liabilities at
fair value on a recurring basis, and certain non-financial assets
and liabilities on a nonrecurring basis. Fair value is defined as the
price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a
liability in the principal or most advantageous market in an orderly
transaction between market participants on the measurement
date. Fair value disclosures are reflected in a three-level hierarchy,
maximizing the use of observable inputs and minimizing the use of
unobservable inputs.
The valuation hierarchy is based upon the transparency of
inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability on the measurement
date. The three levels are defined as follows:
Level 1 – inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted
prices (unadjusted) for an identical asset or liability in an
active market.
Level 2 – inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted
prices for a similar asset or liability in an active market or
model-derived valuations in which all significant inputs are
observable for substantially the full term of the asset or
liability.
Level 3 – inputs to the valuation methodology are
unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement
of the asset or liability.
Certain of the Company’s derivatives are valued using various
pricing models or discounted cash flow analyses that incorporate
observable market parameters, such as interest rate yield curves,
option volatilities and currency rates, classified as Level 2 within
the valuation hierarchy. Derivative valuations incorporate credit
risk adjustments that are necessary to reflect the probability of
default by the counterparty or the Company.
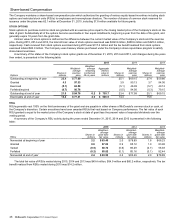
Certain Financial Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair
Value
The following tables present financial assets and liabilities
measured at fair value on a recurring basis by the valuation
hierarchy as defined in the fair value guidance:
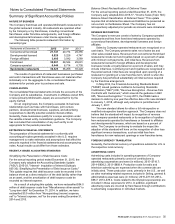
December 31, 2015
In millions Level 1* Level 2
Carrying
Value
Derivative assets $ 139.9 $ 65.4 $ 205.3
Derivative liabilities $ (44.4) $ (44.4)
December 31, 2014
In millions Level 1* Level 2
Carrying
Value
Derivative assets $ 115.9 $ 130.2 $ 246.1
Derivative liabilities $ (50.2) $ (50.2)
* Level 1 is comprised of derivatives that hedge market driven changes in
liabilities associated with the Company’s supplemental benefit plans.
Non-Financial Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair
Value on a Nonrecurring Basis
Certain assets and liabilities are measured at fair value on a
nonrecurring basis; that is, the assets and liabilities are not
measured at fair value on an ongoing basis, but are subject to fair
value adjustments in certain circumstances (e.g., when there is
evidence of impairment). For the year ended December 31, 2015,
the Company recorded fair value adjustments to its long-lived
assets, primarily to goodwill, based on Level 3 inputs which
includes the use of a discounted cash flow valuation approach.
Certain Financial Assets and Liabilities not Measured at
Fair Value
At December 31, 2015, the fair value of the Company’s debt
obligations was estimated at $24.9 billion, compared to a carrying
amount of $24.1 billion. The fair value was based on quoted
market prices, Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy. The carrying
amount for both cash equivalents and notes receivable
approximate fair value.
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES
The Company is exposed to global market risks, including the
effect of changes in interest rates and foreign currency
fluctuations. The Company uses foreign currency denominated
debt and derivative instruments to mitigate the impact of these
changes. The Company does not hold or issue derivatives for
trading purposes.
The Company documents its risk management objective and
strategy for undertaking hedging transactions, as well as all
relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items. The
Company’s derivatives that are designated for hedge accounting
consist mainly of interest rate swaps, foreign currency forwards,
foreign currency options, and cross-currency swaps, and are
classified as either fair value, cash flow or net investment hedges.
Further details are explained in the "Fair Value," "Cash Flow" and
"Net Investment" hedge sections.
The Company also enters into certain derivatives that are not
designated for hedge accounting. The Company has entered into
equity derivative contracts, including total return swaps, to hedge
market-driven changes in certain of its supplemental benefit plan
liabilities. In addition, the Company uses foreign currency forwards
to mitigate the change in fair value of certain foreign currency
denominated assets and liabilities. Further details are explained in
the “Undesignated Derivatives” section.
All derivatives (including those not designated for hedge
accounting) are recognized on the Consolidated balance sheet at
fair value and classified based on the instruments’ maturity dates.
Changes in the fair value measurements of the derivative
instruments are reflected as adjustments to accumulated other
comprehensive income ("AOCI") and/or current earnings.