McDonalds 2015 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 2015 McDonalds annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
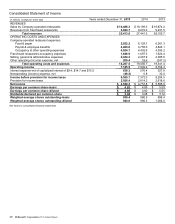
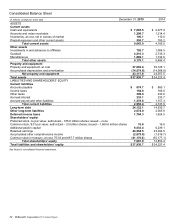
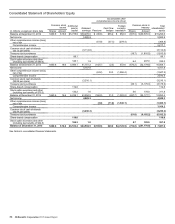
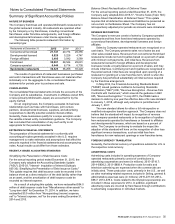
McDonald's Corporation 2015 Annual Report 39
The Company periodically uses interest rate swaps to effectively
convert a portion of floating-rate debt, including forecasted debt
issuances, into fixed-rate debt. The agreements are intended to
reduce the impact of interest rate changes on future interest
expense.
To protect against the reduction in value of forecasted foreign
currency cash flows (such as royalties denominated in foreign
currencies), the Company uses foreign currency forwards and
foreign currency options to hedge a portion of anticipated
exposures. When the U.S. dollar strengthens against foreign
currencies, the decline in value of future foreign denominated
royalties is offset by gains in the fair value of the foreign currency
forwards and/or foreign currency options. Conversely, when the
U.S. dollar weakens, the increase in the value of future foreign
denominated royalties is offset by losses in the fair value of the
foreign currency forwards and/or foreign currency options.
Although the fair value changes in the foreign currency options
may fluctuate over the period of the contract, the Company’s total
loss on a foreign currency option is limited to the upfront premium
paid for the contract; however, the potential gains on a foreign
currency option are unlimited. The hedges cover the next 16
months for certain exposures and are denominated in various
currencies. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had
derivatives outstanding with an equivalent notional amount of
$373.6 million that were used to hedge a portion of forecasted
foreign currency denominated royalties.
The Company uses cross-currency swaps to hedge the risk of
cash flows associated with certain foreign currency denominated
debt, including forecasted interest payments. The hedges cover
periods up to 15 months and have an equivalent notional amount
of $134.7 million.
The Company recorded after tax adjustments to the cash flow
hedging component of AOCI in shareholders’ equity. The
Company recorded a decrease of $11.0 million for the year ended
December 31, 2015 and a net increase of $33.3 million for the
year ended December 31, 2014. Based on interest rates and
foreign exchange rates at December 31, 2015, there is $20.0
million in after-tax cumulative cash flow hedging gains which is not
expected to have a significant effect on earnings over the next
12 months.
Net Investment Hedges
The Company primarily uses foreign currency denominated debt
(third party and intercompany) to hedge its investments in certain
foreign subsidiaries and affiliates. Realized and unrealized
translation adjustments from these hedges are included in the
foreign currency translation component of AOCI, as well as the
offset translation adjustments on the underlying net assets of
foreign subsidiaries and affiliates. The cumulative translation gains
or losses will remain in AOCI until the foreign subsidiaries and
affiliates are liquidated or sold. As of December 31, 2015, $6.2
billion of third party foreign currency denominated debt, $3.4 billion
of intercompany foreign currency denominated debt, and $287.8
million of derivatives were designated to hedge investments in
certain foreign subsidiaries and affiliates.
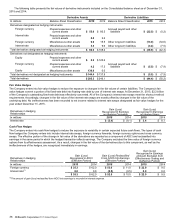
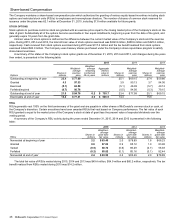
Derivatives in Hedging
Relationships
Gain (Loss)
Recognized in AOCI
(Effective Portion)
In millions 2015 2014
Foreign currency denominated debt $ 668.1 $ 954.6
Foreign currency derivatives 79.1 126.6
$ 747.2 $1,081.2
Undesignated Derivatives
The Company enters into certain derivatives that are not
designated for hedge accounting, therefore the changes in the fair
value of these derivatives are recognized immediately in earnings
together with the gain or loss from the hedged balance sheet
position. As an example, the Company enters into equity
derivative contracts, including total return swaps, to hedge market-
driven changes in certain of its supplemental benefit plan
liabilities. Changes in the fair value of these derivatives are
recorded in Selling, general & administrative expenses together
with the changes in the supplemental benefit plan liabilities. In
addition, the Company uses foreign currency forwards to mitigate
the change in fair value of certain foreign currency denominated
assets and liabilities. The changes in the fair value of these
derivatives are recognized in Nonoperating (income) expense, net,
along with the currency gain or loss from the hedged balance
sheet position.
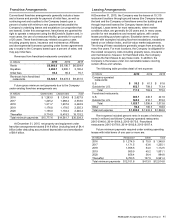
Derivatives Not Designated
for Hedge Accounting
Gain (Loss)
Recognized in Earnings
In millions 2015 2014
Foreign currency $14.6 $ 10.4
Equity 38.9 23.5
$ 53.5 $ 33.9
Credit Risk
The Company is exposed to credit-related losses in the event of
non-performance by the counterparties to its hedging instruments.
The counterparties to these agreements consist of a diverse group
of financial institutions and market participants. The Company
continually monitors its positions and the credit ratings of its
counterparties and adjusts positions as appropriate. The Company
did not have significant exposure to any individual counterparty at
December 31, 2015 and has master agreements that contain
netting arrangements. For financial reporting purposes, the
Company presents gross derivative balances in the financial
statements and supplementary data, even for counterparties
subject to netting arrangements. Some of these agreements also
require each party to post collateral if credit ratings fall below, or
aggregate exposures exceed, certain contractual limits. At
December 31, 2015, the Company was required to post an
immaterial amount of collateral due to certain derivatives having
negative positions. The Company's counterparties were not
required to post collateral on any derivative position, other than on
hedges of certain of the Company’s supplemental benefit plan
liabilities where the counterparties were required to post collateral
on their liability positions.
INCOME TAX UNCERTAINTIES
The Company, like other multi-national companies, is regularly
audited by federal, state and foreign tax authorities, and tax
assessments may arise several years after tax returns have been
filed. Accordingly, tax liabilities are recorded when, in
management’s judgment, a tax position does not meet the more
likely than not threshold for recognition. For tax positions that meet
the more likely than not threshold, a tax liability may still be
recorded depending on management’s assessment of how the tax
position will ultimately be settled.
The Company records interest and penalties on unrecognized
tax benefits in the provision for income taxes.