McDonalds 2013 Annual Report Download - page 48
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 48 of the 2013 McDonalds annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
40 | McDonald’s Corporation 2013 Annual Report
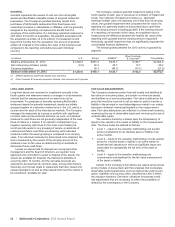
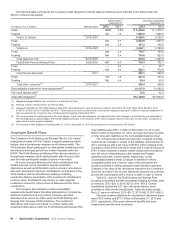
The following table summarizes the Company’s debt obligations (interest rates and debt amounts reflected in the table include the
effects of interest rate swaps).
Interest rates(1)
December 31
Amounts outstanding
December 31
In millions of U.S. Dollars Maturity dates 2013 2012 2013 2012
Fixed 4.6% 4.8% $ 6,460.6 $ 7,075.7
Floating 3.2 1.2 1,900.0 1,650.0
Total U.S. Dollars 2014-2043 8,360.6 8,725.7
Fixed 3.3 3.7 2,884.9 1,847.2
Floating 2.8 2.9 357.2 348.0
Total Euro 2014-2025 3,242.1 2,195.2
Fixed 2.9 2.9 118.7 144.2
Floating 0.4 0.4 759.8 923.3
Total Japanese Yen 2014-2030 878.5 1,067.5
Total British Pounds Sterling-Fixed 2020-2032 6.0 6.0 744.3 730.1
Fixed —3.0 —32.1
Floating 5.4 5.6 525.1 470.8
Total Chinese Renminbi 2014 525.1 502.9
Fixed 1.9 1.9 281.0 273.3
Floating 3.6 4.4 85.4 95.5
Total other currencies(2) 2014-2021 366.4 368.8
Debt obligations before fair value adjustments(3) 14,117.0 13,590.2
Fair value adjustments(4) 12.8 42.3
Total debt obligations(5) $14,129.8 $13,632.5
(1) Weighted-average effective rate, computed on a semi-annual basis.
(2) Primarily consists of Swiss Francs and Korean Won.
(3) Aggregate maturities for 2013 debt balances, before fair value adjustments, were as follows (in millions): 2014–$0.0; 2015–$1,199.2; 2016–$2,094.6; 2017–
$1,054.2; 2018–$1,003.9; Thereafter–$8,765.1. These amounts include a reclassification of short-term obligations totaling $1.2 billion to long-term obligations as
they are supported by a long-term line of credit agreement expiring in November 2016.
(4) The carrying value of underlying items in fair value hedges, in this case debt obligations, are adjusted for fair value changes to the extent they are attributable to
the risk designated as being hedged. The related hedging instrument is also recorded at fair value in prepaid expenses and other current assets, miscellaneous
other assets or other long-term liabilities.
(5) The increase in debt obligations from December 31, 2012 to December 31, 2013 was primarily due to net issuances of $0.5 billion.
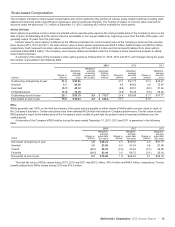
Employee Benefit Plans
The Company’s Profit Sharing and Savings Plan for U.S.-based
employees includes a 401(k) feature, a regular employee match
feature, and a discretionary employer profit sharing match. The
401(k) feature allows participants to make pretax contributions that
are matched each pay period from shares released under the
ESOP. The Profit Sharing and Savings Plan also provides for a
discretionary employer profit sharing match after the end of the
year for those participants eligible to share in the match.
All current account balances and future contributions and
related earnings can be invested in several investment
alternatives as well as McDonald’s common stock in accordance
with each participant’s elections. Participants’ contributions to the
401(k) feature and the discretionary employer matching
contribution feature are limited to 20% investment in McDonald’s
common stock. Participants may choose to make separate
investment choices for current account balances and for future
contributions.
The Company also maintains certain nonqualified
supplemental benefit plans that allow participants to (i) make tax-
deferred contributions and (ii) receive Company-provided
allocations that cannot be made under the Profit Sharing and
Savings Plan because of IRS limitations. The investment
alternatives and returns are based on certain market-rate
investment alternatives under the Profit Sharing and Savings Plan.
Total liabilities were $531.1 million at December 31, 2013, and
$493.5 million at December 31, 2012, and were primarily included
in other long-term liabilities on the Consolidated balance sheet.
The Company has entered into derivative contracts to hedge
market-driven changes in certain of the liabilities. At December 31,
2013, derivatives with a fair value of $128.2 million indexed to the
Company's stock and a total return swap with a notional amount of
$181.4 million indexed to certain market indices were included at
their fair value in Miscellaneous other assets and Prepaid
expenses and other current assets, respectively, on the
Consolidated balance sheet. Changes in liabilities for these
nonqualified plans and in the fair value of the derivatives are
recorded primarily in Selling, general & administrative expenses.
Changes in fair value of the derivatives indexed to the Company’s
stock are recorded in the income statement because the contracts
provide the counterparty with a choice to settle in cash or shares.
Total U.S. costs for the Profit Sharing and Savings Plan,
including nonqualified benefits and related hedging activities, were
(in millions): 2013–$21.9; 2012–$27.9; 2011–$41.3. Certain
subsidiaries outside the U.S. also offer profit sharing, stock
purchase or other similar benefit plans. Total plan costs outside
the U.S. were (in millions): 2013–$51.2; 2012–$62.5; 2011–$58.3.
The total combined liabilities for international retirement plans
were $75.0 million and $77.7 million at December 31, 2013 and
2012, respectively. Other post-retirement benefits and post-
employment benefits were immaterial.