Microsoft 2003 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 37 of the 2003 Microsoft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Part II, Item 8
MSFT 2003 FORM 10-K
24 /
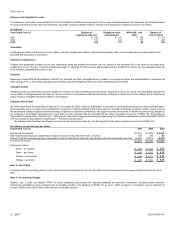
Income Taxes
Income tax expense includes U.S. and international income taxes, plus the provision for U.S. taxes on undistributed earnings of international subsidiaries not
deemed to be permanently invested. Certain items of income and expense are not reported in tax returns and financial statements in the same year. The tax effect
of such temporary differences is reported as deferred income taxes.
Financial Instruments
We consider all highly liquid interest-earning investments with a maturity of three months or less at the date of purchase to be cash equivalents. Short-term
investments generally mature between three months to nine years from the purchase date. Investments with maturities beyond one year may be classified as
short-term based on their highly liquid nature and because such marketable securities represent the investment of cash that is available for current operations. All
cash and short-term investments are classified as available for sale and are recorded at market value using the specific identification method; unrealized gains and
losses are reflected in OCI.
Equity and other investments include debt and equity instruments. Debt securities and publicly traded equity securities are classified as available for sale and
are recorded at market using the specific identification method. Unrealized gains and losses (excluding other-than-temporary impairments) are reflected in OCI. All
other investments, excluding those accounted for using the equity method, are recorded at cost.
We lend certain fixed income and equity securities to enhance investment income. Collateral and/or security interest is determined based upon the underlying
security and the creditworthiness of the borrower. The fair value of collateral that we are permitted to sell or repledge was $499 million at both June 30, 2002 and
2003.
Investments are considered to be impaired when a decline in fair value is judged to be other-than-temporary. We employ a systematic methodology that
considers available evidence in evaluating potential impairment of our investments. If the cost of an investment exceeds its fair value, we evaluate, among other
factors, general market conditions, the duration and extent to which the fair value is less than cost, as well as our intent and ability to hold the investment. We also
consider specific adverse conditions related to the financial health of and business outlook for the investee, including industry and sector performance, changes in
technology, operational and financing cash flow factors, and rating agency actions. Once a decline in fair value is determined to be other-than-temporary, an
impairment charge is recorded and a new cost basis in the investment is established.
We use derivative instruments to manage exposures to foreign currency, security price, interest rate, and credit risks. Our objectives for holding derivatives
include reducing, eliminating, and efficiently managing the impact of these exposures as effectively as possible.
Foreign Currency Risk. Certain forecasted transactions and assets are exposed to foreign currency risk. We monitor our foreign currency exposures daily to
maximize the overall effectiveness of our foreign currency hedge positions. Principal currencies hedged include the Euro, Japanese yen, British pound, and
Canadian dollar. Non U.S. dollar denominated securities are hedged using foreign exchange forward contracts that are designated as fair value hedging
instruments under SFAS 133. Options used to hedge a portion of forecasted international revenue for up to three years in the future are designated as cash flow
hedging instruments. Certain options and forwards not designated as hedging instruments under SFAS 133 are also used to hedge the impact of the variability in
exchange rates on accounts receivable and collections denominated in certain foreign currencies.
Securities Price Risk. Strategic equity investments are subject to market price risk. From time to time, we use and designate options to hedge fair values and
cash flows on certain equity securities. We determine the security, or forecasted sale thereof, selected for hedging by market conditions, up-front costs, and other
relevant factors. Once established, the hedges are not dynamically managed or traded, and are generally not removed until maturity.
Interest Rate Risk. Fixed-income securities are subject to interest rate risk. The fixed-income portfolio is diversified and consists primarily of investment grade
securities to minimize credit risk. We use exchange-traded option and future contracts, not designated as hedging instruments under SFAS 133, to hedge interest
rate risk. In addition, we routinely use options, not designated as hedging instruments under SFAS 133, to hedge our exposure to interest rate risk in the event of a
catastrophic increase in interest rates.
Other Derivatives. Swap contracts, not designated as hedging instruments under SFAS 133, are used to manage exposures to credit risks. In addition, we may
invest in warrants to purchase securities of other companies as a strategic investment. Warrants that can be net share settled are deemed derivative financial
instruments and are not designated as hedging instruments. To Be Announced forward purchase commitments of mortgage-backed assets are also considered
derivatives in cases where physical delivery of the assets are not taken at the earliest available delivery date.
For options designated either as fair value or cash flow hedges, changes in the time value are excluded from the assessment of hedge effectiveness.