Starbucks 2013 Annual Report Download - page 46
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 46 of the 2013 Starbucks annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
38
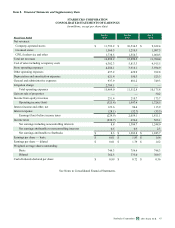
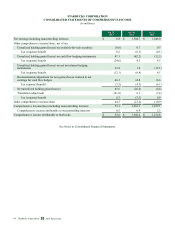
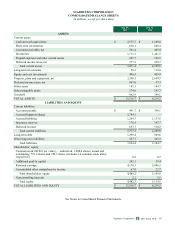
COMMODITY PRICES, AVAILABILITY AND GENERAL RISK CONDITIONS
Commodity price risk represents Starbucks primary market risk, generated by our purchases of green coffee and dairy products,
among other items. We purchase, roast and sell high-quality whole bean arabica coffee and related products and risk arises
from the price volatility of green coffee. In addition to coffee, we also purchase significant amounts of dairy products to
support the needs of our company-operated stores. The price and availability of these commodities directly impact our results
of operations and we expect commodity prices, particularly coffee, to impact future results of operations. For additional details
see Product Supply in Item 1, as well as Risk Factors in Item 1A of this 10-K.
FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT
Market risk is defined as the risk of losses due to changes in commodity prices, foreign currency exchange rates, equity
security prices, and interest rates. We manage our exposure to various market-based risks according to a market price risk
management policy. Under this policy, market-based risks are quantified and evaluated for potential mitigation strategies, such
as entering into hedging transactions. The market price risk management policy governs how hedging instruments may be used
to mitigate risk. Risk limits are set annually and prohibit speculative trading activity. We also monitor and limit the amount of
associated counterparty credit risk. In general, hedging instruments do not have maturities in excess of five years.
The sensitivity analyses disclosed below provide only a limited, point-in-time view of the market risk of the financial
instruments discussed. The actual impact of the respective underlying rates and price changes on the financial instruments may
differ significantly from those shown in the sensitivity analyses.
Commodity Price Risk
We purchase commodity inputs, including coffee, dairy products and diesel that are used in our operations and are subject to
price fluctuations that impact our financial results. In addition to fixed-price and price-to-be-fixed contracts for coffee
purchases, we have entered into commodity hedges to manage commodity price risk using financial derivative instruments.
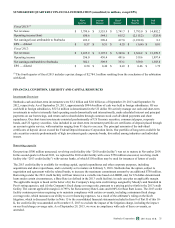
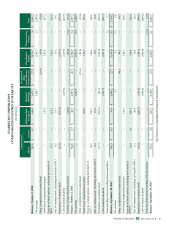
The following table summarizes the potential impact as of September 29, 2013 to Starbucks future net earnings and other
comprehensive income (“OCI”) from changes in commodity prices. The information provided below relates only to the
hedging instruments and does not represent the corresponding changes in the underlying hedged items (in millions):
Increase/(Decrease) to Net Earnings Increase/(Decrease) to OCI
10% Increase in
Underlying Rate
10% Decrease in
Underlying Rate
10% Increase in
Underlying Rate
10% Decrease in
Underlying Rate
Commodity hedges $ 6 $ (6) $ — $ —
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
The majority of our revenue, expense and capital purchasing activities are transacted in US dollars. However, because a portion
of our operations consists of activities outside of the US, we have transactions in other currencies, primarily the Canadian
dollar, Japanese yen, Chinese renminbi, British pound, and euro. As a result, we may engage in transactions involving various
derivative instruments to hedge revenues, inventory purchases, assets, and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies.
As of September 29, 2013, we had forward foreign exchange contracts that hedge portions of anticipated international revenue
streams and inventory purchases. In addition, we had forward foreign exchange contracts that qualify as accounting hedges of
our net investment in Starbucks Japan to minimize foreign currency exposure.
Starbucks also had forward foreign exchange contracts that are not designated as hedging instruments for accounting purposes
(free standing derivatives), but which largely offset the financial impact of translating certain foreign currency denominated
payables and receivables. Increases or decreases in the fair value of these derivatives are generally offset by corresponding
decreases or increases in the US dollar value of our foreign currency denominated payables and receivables (i.e., “hedged
items”) that would occur within the period.
2013 10-K
Starbucks Corporation Form