Humana 2007 Annual Report Download - page 32
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 32 of the 2007 Humana annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Our industry is currently subject to substantial government regulation, which, along with possible
increased governmental regulation or legislative reform, increases our costs of doing business and could
adversely affect our profitability.
The health care industry in general, and health insurance, particularly HMOs and PPOs are subject to
substantial federal and state government regulation.
Our licensed subsidiaries are subject to regulation under state insurance holding company and Puerto Rico
regulations. These regulations generally require, among other things, prior approval and/or notice of new
products, rates, benefit changes, and certain material transactions, including dividend payments, purchases or
sales of assets, intercompany agreements, and the filing of various financial and operational reports.
Certain of our subsidiaries operate in states that regulate the payment of dividends, loans, or other cash
transfers to Humana Inc., our parent company, and require minimum levels of equity as well as limit investments
to approved securities. The amount of dividends that may be paid to Humana Inc. by these subsidiaries, without
prior approval by state regulatory authorities, is limited based on the entity’s level of statutory income and
statutory capital and surplus. In most states, prior notification is provided before paying a dividend even if
approval is not required.
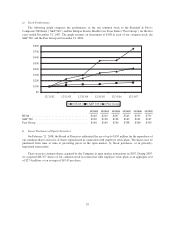
Based on the most recent statutory financial statements as of December 31, 2007, we maintained aggregate
statutory capital and surplus of $2,905.2 million in our state regulated subsidiaries. This compares to applicable
statutory requirements which aggregated $1,810.5 million. Although the minimum required levels of equity are
largely based on premium volume, product mix, and the quality of assets held, minimum requirements can vary
significantly at the state level. Given our anticipated continued premium growth in 2008, capital requirements
will increase. We expect to fund these increased requirements with capital contributions from Humana Inc., our
parent company, of approximately $200 million in 2008.
Most states rely on risk-based capital requirements, or RBC, to define their required levels of equity
discussed above. RBC is a model developed by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners to monitor
an entity’s solvency. This calculation indicates recommended minimum levels of required capital and surplus and
signals regulatory measures should actual surplus fall below these recommended levels. If RBC were adopted by
the remaining states and Puerto Rico at December 31, 2007, we would have $966.3 million of aggregate capital
and surplus above any of the levels that require corrective action under RBC, or individual state requirements
based on the most recent statutory financial statements as of December 31, 2007.
The use of individually identifiable health data by our business is regulated at federal and state levels. These
laws and rules are changed frequently by legislation or administrative interpretation. Various state laws address
the use and maintenance of individually identifiable health data. Most are derived from the privacy provisions in
the federal Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and HIPAA. HIPAA includes administrative provisions directed at
simplifying electronic data interchange through standardizing transactions, establishing uniform health care
provider, payer, and employer identifiers and seeking protections for confidentiality and security of patient data.
The rules do not provide for complete federal preemption of state laws, but rather preempt all inconsistent state
laws unless the state law is more stringent.
These regulations set standards for the security of electronic health information. Violations of these rules
could subject us to significant criminal and civil penalties, including significant monetary penalties. Compliance
with HIPAA regulations requires significant systems enhancements, training and administrative effort. HIPAA
could also expose us to additional liability for violations by our business associates. A business associate is a
person or entity, other than a member of the work force, who on behalf of a covered entity performs or assists in
the performance of a function or activity involving the use or disclosure of individually identifiable health
information, or provides legal, accounting, consulting, data aggregation, management, administrative,
accreditation, or financial services.
22