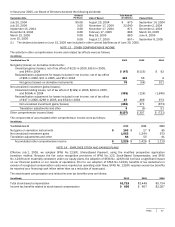
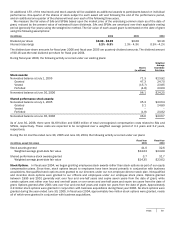
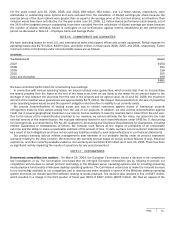
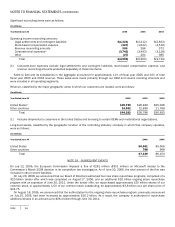
Microsoft 2006 Annual Report Download - page 66
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 66 of the 2006 Microsoft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
PAGE 65
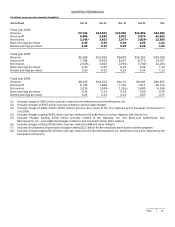
SFAS No. 131, Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information, establishes standards for reporting
information about operating segments. This standard requires segmentation based on our internal organization and reporting of
revenue and operating income based upon internal accounting methods. Our financial reporting systems present various data
for management to operate the business, including internal profit and loss statements prepared on a basis not consistent with
U.S. GAAP. Fiscal years 2005 and 2004 amounts have been restated for certain internal reorganizations and to conform to the
current period presentation. The segments are designed to allocate resources internally and provide a framework to determine
management responsibility. Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise about which separate financial
information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker, or decision making group, in deciding
how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. Our chief operating decision maker is our Chief Executive Officer. Our
seven segments are Client; Server and Tools; Information Worker; Microsoft Business Solutions; MSN; Mobile and Embedded
Devices; and Home and Entertainment. On July 17, 2006 we announced a change in our operating segments reflecting the
culmination of our realignment announced in September 2005. These changes will be effective for fiscal year 2007; the seven
segments discussed in this analysis are presented the way we internally managed and monitored performance at the business
group level in fiscal years 2006, 2005, and 2004.
The types of products and services provided by each segment are summarized below:
Client – Windows XP Professional and Home; Media Center Edition; Tablet PC Edition; and other standard Windows operating
systems.
Server and Tools – Windows Server operating system; Microsoft SQL Server; Exchange Server; Microsoft Consulting Services;
product support services; Visual Studio; System Center products, Forefront security family of products; and Biz Talk.
Information Worker – Microsoft Office; Microsoft Project; Microsoft Visio; SharePoint Portal Server client access licenses;
Microsoft LiveMeeting; OneNote; and Office Communication Server.
Microsoft Business Solutions – Microsoft Dynamics AX; Microsoft Dynamics CRM; Microsoft Dynamics GP; Microsoft Dynamics
NAV; Microsoft Dynamics SL; Microsoft Dynamics Retail Management System; Microsoft Partner Program; and Microsoft Office
Small Business Accounting.
MSN – MSN Search; MapPoint; MSN Internet Access; MSN Premium Web Services (consisting of MSN Internet Software
Subscription, MSN Hotmail Plus, MSN Bill Pay, and MSN Radio Plus); and MSN Mobile Services.
Mobile and Embedded Devices – Windows Mobile software platform; Windows Embedded device operating system; and
Windows Automotive.
Home and Entertainment – Xbox 360; Xbox; Xbox Live; CPxG (consumer software and hardware products); and IPTV.
Because of our integrated business structure, operating costs included in one segment may benefit other segments, and
therefore these segments are not designed to measure operating income or loss directly related to the products included in
each segment. Inter-segment cost commissions are estimated by management and used to compensate or charge each
segment for such shared costs and to incent shared efforts. Management will continually evaluate the alignment of product
development organizations, sales organizations, and inter-segment commissions for segment reporting purposes, which may
result in changes to segment allocations in future periods.
Assets are not allocated to segments for internal reporting presentations. A portion of amortization and depreciation is
included with various other costs in an overhead allocation to each segment and it is impracticable for us to separately identify
the amount of amortization and depreciation by segment that is included in the measure of segment profit or loss.
Reconciling amounts include adjustments to conform with U.S. GAAP and corporate-level activity not specifically attributed to
a segment. Significant internal accounting policies that differ from U.S. GAAP relate to revenue recognition, income statement
classification, period-end cut-off timing, and accelerated amortization for depreciation, stock awards, and performance-based
stock awards. In addition, certain revenue and expenses are excluded from segments or included in corporate-level activity
including certain legal settlements and accruals for legal contingencies.