Safeway 2011 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2011 Safeway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SAFEWAY INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
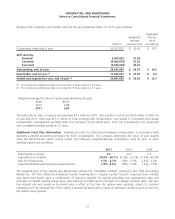
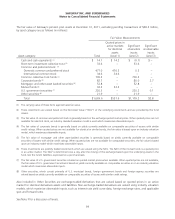
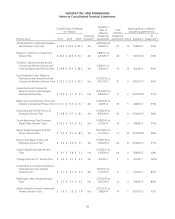
The fair value of Safeway’s pension plan assets at December 31, 2011, excluding pending transactions of $28.2 million,
by asset category are as follows (in millions):
Fair Value Measurements
Asset category: Total
Quoted prices in
active markets
for identical
assets
(Level 1)
Significant
observable
inputs
(Level 2)
Significant
unobservable
inputs
(Level 3)
Cash and cash equivalents (1) $ 14.1 $ 14.2 $ (0.1) $ –
Short-term investment collective trust (2) 33.6 – 33.6 –
Common and preferred stock: (3)
Domestic common and preferred stock 477.0 476.5 0.5 –
International common stock 34.6 34.6 – –
Common collective trust funds (2) 700.3 – 700.3 –
Corporate bonds (4) 82.7 – 80.0 2.7
Mortgage- and other-asset backed securities (5) 52.8 – 52.8 –
Mutual funds (6) 32.3 32.3 – –
U.S. government securities (7) 220.3 – 220.2 0.1
Other securities (8) 21.9 – 21.9 –
Total $1,669.6 $557.6 $1,109.2 $2.8
(1) The carrying value of these items approximates fair value.
(2) These investments are valued based on the Net Asset Value (“NAV”) of the underlying investments and are provided by the fund
issuers.
(3) The fair value of common and preferred stock is generally based on the exchange quoted market prices. When quoted prices are not
available for identical stock, an industry standard valuation model is used which maximizes observable inputs.
(4) The fair value of corporate bonds is generally based on yields currently available on comparable securities of issuers with similar
credit ratings. When quoted prices are not available for identical or similar bonds, the fair value is based upon an industry valuation
model, which maximizes observable inputs.
(5) The fair value of mortgage- and other asset-backed securities is generally based on yields currently available on comparable
securities of issuers with similar credit ratings. When quoted prices are not available for comparable securities, the fair value is based
upon an industry model which maximizes observable inputs.
(6) These investments are publicly traded investments which are valued using the NAV. The NAV of the mutual funds is a quoted price
in an active market. The NAV is determined once a day after the closing of the exchange based upon the underlying assets in the
fund, less the fund’s liabilities, expressed on a per-share basis.
(7) The fair value of U.S. government securities is based on quoted market prices when available. When quoted prices are not available,
the fair value of U.S. government securities is based on yields currently available on comparable securities or on an industry valuation
model which maximizes observable inputs.
(8) Other securities, which consist primarily of U.S. municipal bonds, foreign government bonds and foreign agency securities are
valued based on yields currently available on comparable securities of issuers with similar credit ratings.
Also included in Other Securities are exchange-traded derivatives that are valued based on quoted prices in an active
market for identical derivatives assets and liabilities. Non-exchange-traded derivatives are valued using industry valuation
models, which maximize observable inputs, such as interest-rate yield curve data, foreign exchange rates, and applicable
spot and forward rates.
See Note F for a discussion of levels.
64