Walmart 2007 Annual Report Download - page 47
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 47 of the 2007 Walmart annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Wal-Mart 2007 Annual Report 45
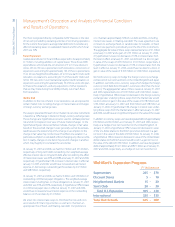
Operating, Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Operating, selling, general and administrative expenses include all
operating costs of the Company except those costs related to the
transportation of products from the supplier to the warehouses, stores
or clubs, the costs related to the transportation of products from the
warehouses to the stores or clubs and the cost of warehousing for
our Sam’s Club segment. As a result, the cost of warehousing and
occupancy for our Wal-Mart Stores and International segments distri-
bution facilities are included in operating, selling, general and
administrative expenses. Because we do not include the cost of our
Wal-Mart Stores and International segments distribution facilities in
cost of sales, our gross pro t and gross margin may not be compara-
ble to those of other retailers that may include all costs related to their
distribution facilities in costs of sales and in the calculation of gross
pro t and gross margin.
Advertising Costs
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and were $1.9 billion, $1.6 bil-
lion and $1.4 billion in fiscal 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively.
Advertising costs consist primarily of print and television advertisements.
Pre-Opening Costs
The costs of start-up activities, including organization costs and new
store openings, are expensed as incurred.
Share-Based Compensation
The Company recognizes expense for its share-based compensation
based on the fair value of the awards that are granted. The fair value
of stock options is estimated at the date of grant using the Black-
Scholes-Merton option valuation model which was developed for
use in estimating the fair value of exchange traded options that have
no vesting restrictions and are fully transferable. Option valuation
methods require the input of highly subjective assumptions, includ-
ing the expected stock price volatility. Measured compensation cost,
net of estimated forfeitures, is recognized ratably over the vesting
period of the related share-based compensation award.
Share-based compensation awards that may be settled in cash are
accounted for as liabilities and marked to market each period. Measured
compensation cost for performance-based awards is recognized only
if it is probable that the performance condition will be achieved.
Insurance/Self-lnsurance
The Company uses a combination of insurance, self-insured retention
and self-insurance for a number of risks, including, without limitation,
workers’ compensation, general liability, vehicle liability and the
Company’s obligation for employee-related healthcare benefits.
Liabilities associated with these risks are estimated by considering
historical claims experience, demographic factors, frequency and
severity factors and other actuarial assumptions.
Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation and amortization for nancial statement purposes are
provided on the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives
of the various assets. Depreciation expense, including amortization of
property under capital leases for scal years 2007, 2006 and 2005 was
$5.5 billion, $4.6 billion and $4.2 billion, respectively. For income tax
purposes, accelerated methods of depreciation are used with recog-
nition of deferred income taxes for the resulting temporary di erences.
Leasehold improvements are depreciated over the shorter of the
estimated useful life of the asset or the remaining expected lease term.
Estimated useful lives for nancial statement purposes are as follows:
Buildings and improvements 5–50 years
Fixtures and equipment 3–12 years
Transportation equipment 3–15 years
Income Taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated
future tax consequences attributable to di erences between the
nancial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities
and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are
measured using enacted tax rates in e ect for the year in which
those temporary di erences are expected to be recovered or settled.
The e ect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rate
is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment
date. Valuation allowances are established when necessary to reduce
deferred tax assets to the amounts more likely than not to be realized.
In determining the quarterly provision for income taxes, the Company
uses an annual e ective tax rate based on expected annual income
and statutory tax rates. The e ective tax rate also re ects the Company’s
assessment of the ultimate outcome of tax audits. Signi cant discrete
items are separately recognized in the income tax provision in the
quarter in which they occur.
The determination of the Company’s provision for income taxes requires
signi cant judgment, the use of estimates, and the interpretation and
application of complex tax laws. Signi cant judgment is required in
assessing the timing and amounts of deductible and taxable items.
Reserves are established when, despite management’s belief that the
Company’s tax return positions are fully supportable, management
believes that certain positions may be successfully challenged. When
facts and circumstances change, these reserves are adjusted through
the provision for income taxes.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements