Sony 1999 Annual Report Download - page 54
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 54 of the 1999 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
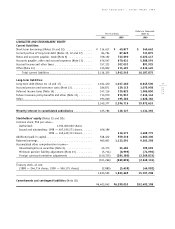
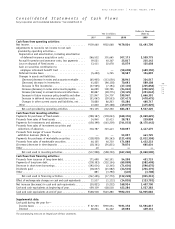
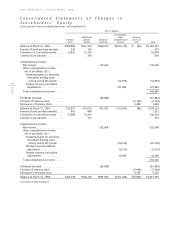
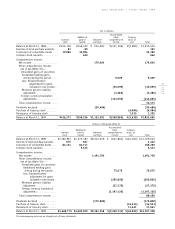
52
page
Sony Corporation Annual Report 1999
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Sony Corporation and Consolidated Subsidiaries
1. Nature of operations
Sony Corporation and consolidated subsidiaries (herein-
after collectively referred to as “Sony”) is engaged in the
development, design, manufacture, and sale of various
kinds of electronic equipment, instruments, and devices
for consumer and industrial markets. Sony’s principal
manufacturing facilities are located in Japan, the United
States, Europe, and Asia, and its products are marketed
by sales subsidiaries and unaffiliated local distributors
throughout the world. Sony also develops, produces,
manufactures, and markets home-use game consoles and
software. Sony is engaged in the development, produc-
tion, manufacture, and distribution of recorded music,
in all commercial formats and musical genres. Sony is
also engaged in the development, production, manufac-
ture, marketing, distribution and broadcasting of image-
based software, including film, video, and television.
Further, Sony conducts insurance operations principally
through a Japanese stock life insurance subsidiary. In
addition to the above, Sony is engaged in leasing and
credit card businesses, satellite distribution services
including program supplying businesses in Japan,
internet-related businesses, development of location-
based entertainment complexes, and others.
2. Summary of significant accounting policies
Sony Corporation and its subsidiaries in Japan maintain
their records and prepare their financial statements in
accordance with accounting principles generally ac-
cepted in Japan while its foreign subsidiaries maintain
their records and prepare their financial statements in
conformity with accounting principles generally accepted
in the countries of their domiciles. Certain adjustments
and reclassifications, including those relating to the tax
effects of temporary differences, capitalization of stock
purchase warrants, deferral of insurance acquisition
costs and the accrual of certain expenses, have been
incorporated in the accompanying consolidated financial
statements to conform with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States of America (U.S.
GAAP). These adjustments were not recorded in the
statutory books of account.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity
with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates
and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of
assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets
and liabilities at the date of the financial statements
and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses dur-
ing the reporting period. Actual results could differ from
those estimates.
Significant accounting policies are as follows:
Basis of consolidation and accounting for
investments in affiliated companies
The consolidated financial statements include the
accounts of Sony Corporation and those of its majority-
owned subsidiary companies. All intercompany transac-
tions and accounts are eliminated. Investments in 20%
to 50% owned companies are stated at cost plus/minus
equity in undistributed earnings/losses; consolidated
net income includes Sony’s equity in current earnings/
losses of such companies, after elimination of unrealized
intercompany profits.
On occasion, a subsidiary or affiliated company
accounted for by the equity method may issue its shares
to third parties as either a public offering or upon con-
version of convertible debt to common stock at amounts
per share in excess of or less than Sony’s average per
share carrying value. With respect to such transactions,
the resulting gains or losses arising from the change in
interest are recorded in income for the year the change
in interest transaction occurs.
The excess of the cost over the underlying net equity
of investments in subsidiaries and affiliated companies
accounted for on an equity basis is allocated to identifi-
able assets based on fair values at the date of acquisi-
tion. The unassigned residual value of the excess of the
cost over the underlying net equity is recognized as
goodwill.
Translation of foreign currencies
All asset and liability accounts of foreign subsidiaries
and affiliates are translated into Japanese yen at appro-
priate year-end current rates and all income and expense
accounts are translated at rates that approximate those
rates prevailing at the time of the transactions. The
resulting translation adjustments are accumulated as a
component of accumulated other comprehensive income.
Foreign currency receivables and payables are trans-
lated at appropriate year-end current rates and the
resulting translation gains or losses are taken into
income currently.
Revenue recognition
Revenues from electronics, game and music sales are
recognized when products are shipped to customers.
Motion picture revenue is recognized beginning on the
date of theatrical exhibition. Revenue from television
licensing agreements is recognized when the motion
picture or television series first becomes available for
telecast. Revenue from home videocassette sales is
generally recognized on the date of shipment.
Insurance premiums are reported as revenue when
due from policyholders. Benefits and expenses are
associated with earned insurance premiums so as to
result in the recognition of profits over the life of the
contracts. This association is accomplished through a
provision for liabilities for future benefits and amortiza-
tion of acquisition costs.