Sony 1999 Annual Report Download - page 55
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 55 of the 1999 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
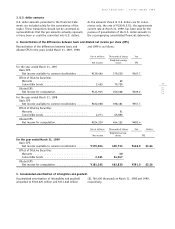
53
page
Sony Corporation Annual Report 1999
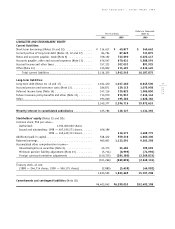
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include all highly liquid in-
vestments, generally with original maturities of three
months or less, that are readily convertible to known
amounts of cash and are so near maturity that they
present insignificant risk of changes in value because of
changes in interest rates.
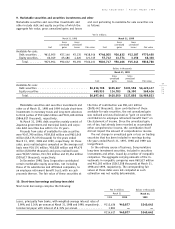
Marketable securities
Marketable securities consist of debt and equity securi-
ties. Debt securities and equity securities designated as
available-for-sale, whose fair values are readily deter-
minable, are carried at fair value with unrealized gains
or losses included as a component of accumulated other
comprehensive income, net of applicable taxes. Debt
and equity securities classified as trading securities are
carried at fair value with unrealized gains or losses in-
cluded in income. Debt securities that are expected to
be held-to-maturity are carried at amortized cost. Indi-
vidual securities classified as either available-for-sale or
held-to-maturity are reduced to net realizable value by a
charge to income for other than temporary declines in
fair value. Realized gains and losses are determined on
the average cost method and are reflected in income.
Inventories
Inventories in electronics, game and music are valued at
cost, not in excess of market, cost being determined on
the “average cost” basis except for the cost of finished
products carried by certain subsidiary companies which
is determined on the “first-in, first-out” basis.
Film costs include production, print, certain advertis-
ing costs and allocated overhead. Film costs are amor-
tized in the proportion that revenue for a period relates
to management’s estimate of ultimate revenues.
Unamortized film costs are compared with estimated
net realizable value on an individual film basis and write-
downs are recorded when indicated. Film costs for motion
pictures and television programs that are expected to be
amortized against revenues from primary markets are
classified as current assets. Primary markets for motion
pictures include theatrical, home videocassette and pay
television. Primary markets for television programs
include network and first-run syndication. All other film
costs are classified as noncurrent.
Property, plant and equipment and depreciation
Property, plant and equipment is stated at cost. Depre-
ciation of property, plant and equipment is computed on
the declining-balance method for Sony Corporation and
Japanese subsidiaries and on the straight-line method
for foreign subsidiary companies at rates based on esti-
mated useful lives of the assets according to general
class, type of construction and use. Significant renewals
and additions are capitalized at cost. Maintenance and
repairs, and minor renewals and betterments are charged
to income as incurred.
Intangibles and goodwill
Intangibles, which mainly consist of artist contracts and
music catalogs, are being amortized on a straight-line
basis principally over 16 years and 21 years, respectively.
Goodwill recognized in acquisitions accounted for as
purchases is being amortized on a straight-line basis
principally over a 40-year period.
Deferred insurance acquisition costs
Costs that vary with and are primarily related to acquir-
ing new insurance policies are deferred and are being
amortized mainly over the premium-paying period of the
related insurance policies using assumptions consistent
with those used in computing policy reserves.
Future insurance policy benefits
Future insurance policy benefits are computed based on
actuarial assumptions.
Accounting for the impairment of long-lived assets
Sony’s long-lived assets, including goodwill and identifi-
able intangibles, held and used are reviewed for impair-
ment whenever events or changes in circumstances
indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not
be recoverable. When the sum of expected future cash
flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) is
less than the carrying amount of the asset, an impair-
ment loss is recognized, based on the fair value of the
asset. The fair value of goodwill is determined using a
discounted cash flows analysis.
Income taxes
The provision for income taxes is computed based on
the pretax income included in the consolidated state-
ments of income. The asset and liability approach is
used to recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for
the expected future tax consequences of temporary
differences between the carrying amounts and the tax
bases of assets and liabilities.
Derivative financial instruments
Derivative financial instruments, which include foreign
exchange forward contracts, foreign currency option
contracts, interest rate swap agreements, and interest
rate and currency swap agreements, are used in Sony’s
risk management of foreign currency and interest rate
risk exposures of its financial assets and liabilities.
Foreign exchange forward contracts
Foreign exchange forward contracts are used to limit
exposure to losses, resulting from changes in foreign
currency exchange rates, on accounts receivable and
payable and anticipated transactions denominated in
foreign currencies. Foreign exchange forward con-
tracts which are designated and effective as hedges
of such currency exchange rate risk on existing assets
and liabilities are marked to market and included as
an offset to foreign exchange gains/losses recorded