Facebook 2013 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2013 Facebook annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
66
FACEBOOK, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Organization and Description of Business
Facebook was incorporated in Delaware in July 2004. Our mission is to give people the power to share and make the world more
open and connected. We build products that support our mission by providing value to Facebook users, marketers, and developers. We
generate substantially all of our revenue from advertising and from fees associated with our Payments infrastructure that enables users
to purchase virtual and digital goods from developers with applications on the Facebook website.
Basis of Presentation
We prepared the consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). The
consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Facebook, Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances
and transactions have been eliminated.
Use of Estimates
Conformity with GAAP requires the use of estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts in the consolidated financial
statements and accompanying notes. These estimates form the basis for judgments we make about the carrying values of our assets and
liabilities, which are not readily apparent from other sources. We base our estimates and judgments on historical information and on
various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. GAAP requires us to make estimates and judgments
in several areas, including, but not limited to, those related to revenue recognition, collectability of accounts receivable, contingent
liabilities, fair value of acquired intangible assets and goodwill, useful lives of intangible assets and property and equipment, and income
taxes. These estimates are based on management's knowledge about current events and expectations about actions we may undertake in
the future. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Reclassifications
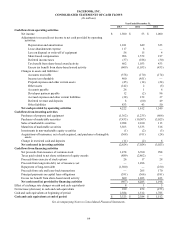
We have reclassified certain prior period amounts within our consolidated statements of cash flows to conform to our current year
presentation.
Revenue Recognition
We generate substantially all of our revenue from advertising and payment processing fees. We recognize revenue once all of the
following criteria have been met:
• persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists;
• delivery of our obligations to our customer has occurred;
• the price is fixed or determinable; and
• collectability of the related receivable is reasonably assured.
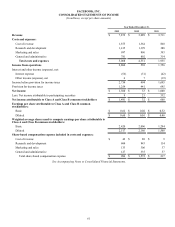
Revenue for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011 consists of the following (in millions):
Year Ended December 31,
2013 2012 2011
Advertising $ 6,986 $ 4,279 $ 3,154
Payments and other fees 886 810 557
Total revenue $ 7,872 $ 5,089 $ 3,711
Advertising
Advertising revenue is generated by displaying ad products on the Facebook website or mobile application and third-party affiliated
websites or mobile applications. The arrangements are evidenced by either online acceptance of terms and conditions or contracts that
stipulate the types of advertising to be delivered, the timing and the pricing. Marketers pay for ad products either directly or through their
relationships with advertising agencies, based on the number of clicks made by our users, the number of actions taken by our users or