Apple 2006 Annual Report Download - page 94
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 94 of the 2006 Apple annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Note 3—Financial Instruments (Continued)
Accounts Receivable
Trade Receivables
The Company distributes its products through third-
party distributors and resellers and directly to certain education, consumer, and commercial
customers. The Company generally does not require collateral from its customers; however, the Company will require collateral in certain
instances to limit credit risk. In addition, when possible, the Company does attempt to limit credit risk on trade receivables with credit
insurance for certain customers in Latin America, Europe, Asia, and Australia and by arranging with third-party financing companies to
provide flooring arrangements and other loan and lease programs to the Company’s direct customers. These credit-financing arrangements are
directly between the third-party financing company and the end customer. As such, the Company generally does not assume any recourse or
credit risk sharing related to any of these arrangements. However, considerable trade receivables that are not covered by collateral, third-party
flooring arrangements, or credit insurance are outstanding with the Company’s distribution and retail channel partners. No customer accounted
for more than 10% of trade receivables as of September 30, 2006 or September 24, 2005.
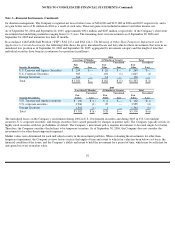
The following table summarizes the activity in the allowance for doubtful accounts (in millions):
(a)
Represents amounts written off against the allowance, net of recoveries.
Vendor Non-Trade Receivables
The Company has non-trade receivables from certain of its manufacturing vendors resulting from the sale of raw material components to these
manufacturing vendors who manufacture sub-assemblies or assemble final products for the Company. The Company purchases these raw
material components directly from suppliers. These non-trade receivables, which are included in the consolidated balance sheets in other
current assets, totaled $1.6 billion and $417 million as of September 30, 2006 and September 24, 2005, respectively. The Company does not
reflect the sale of these components in net sales and does not recognize any profits on these sales until the products are sold through to the end
customer at which time the profit is recognized as a reduction of cost of sales.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company uses derivatives to partially offset its business exposure to foreign exchange risk. Foreign currency forward and option contracts
are used to offset the foreign exchange risk on certain existing assets and liabilities and to hedge the foreign exchange risk on expected future
cash flows on certain forecasted revenue and cost of sales. From time to time, the Company enters into interest rate derivative agreements to
modify the interest rate profile of certain investments and debt. The Company’s accounting policies for these instruments are based on whether
the instruments are designated as hedge or non-hedge instruments. The Company records all derivatives on the balance sheet at fair value.
93
September 30,
2006
September 24,
2005
September 25,
2004
Beginning allowance balance
$
46
$
47
$
49
Charged to costs and expenses
17
8
3
Deductions(a)
(11
)
(9
)
(5
)
Ending allowance balance
$
52
$
46
$
47