Safeway 2012 Annual Report Download - page 61
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 61 of the 2012 Safeway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SAFEWAY INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
49
Income Taxes Income tax expense or benefit reflects the amount of taxes payable or refundable for the
current year, the impact of deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets, accrued interest on tax deficiencies
and refunds and accrued penalties on tax deficiencies. Deferred income taxes represent future net tax effects
resulting from temporary differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities
using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse.
A valuation allowance is established for deferred tax assets if it is more likely than not that these items will
either expire before the Company is able to realize their benefits, or that future deductibility is uncertain.
Periodically, the valuation allowance is reviewed and adjusted based on management's assessments of
realizable deferred tax assets.
Tax positions are recognized when they are more likely than not to be sustained upon examination. The
amount recognized is measured as the largest amount of benefit that is more likely than not of being realized
upon settlement. The Company is subject to periodic audits by the Internal Revenue Service and other
foreign, state and local taxing authorities. These audits may challenge certain of the Company’s tax positions
such as the timing and amount of income and deductions and the allocation of taxable income to various
tax jurisdictions. The Company evaluates its tax positions and establishes liabilities in accordance with the
applicable accounting guidance on uncertainty in income taxes. These tax uncertainties are reviewed as
facts and circumstances change and are adjusted accordingly. This requires significant management
judgment in estimating final outcomes. Actual results could materially differ from these estimates and could
significantly affect the Company’s effective tax rate and cash flows in future years.
Financial Instruments
Interest rate swaps. The Company has, from time to time, entered into interest rate swap agreements to
change its portfolio mix of fixed- and floating-rate debt to more desirable levels. Interest rate swap agreements
involve the exchange with a counterparty of fixed- and floating-rate interest payments periodically over the
life of the agreements without exchange of the underlying notional principal amounts. The differential to be
paid or received is recognized over the life of the agreements as an adjustment to interest expense. The
Company’s counterparties have been major financial institutions.
Energy contracts. The Company has entered into contracts to purchase electricity and natural gas at fixed
prices for a portion of its energy needs. Safeway expects to take delivery of the electricity and natural gas
in the normal course of business. Contracts that qualify for the normal purchase exception under derivatives
and hedging accounting guidance are not marked to market. Energy purchased under these contracts is
expensed as delivered.
Warrants. Blackhawk issued warrants to third parties to purchase shares of Blackhawk common stock. The
warrants are accounted for as liability awards and marked to market every period. The liability is calculated
using the Black-Scholes model and included in accrued claims and other liabilities on the balance sheet. Since
there is no active market for these warrants, the valuation model uses unobservable pricing inputs and
management estimates.
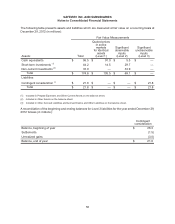
Fair Value of Financial Instruments Disclosures of the fair value of certain financial instruments are
required, whether or not recognized in the balance sheet. The Company estimated the fair values presented
below using appropriate valuation methodologies and market information available as of year end.
Considerable judgment is required to develop estimates of fair value, and the estimates presented are not
necessarily indicative of the amounts that the Company could realize in a current market exchange. The
use of different market assumptions or estimation methodologies could have a material effect on the estimated
fair values. Additionally, the fair values were estimated at year end, and current estimates of fair value may
differ significantly from the amounts presented.