Sony 1997 Annual Report Download - page 53
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 53 of the 1997 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
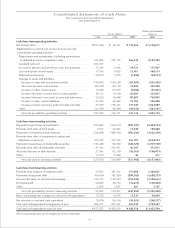
51
The company’s stock life insurance subsidiary maintains accounting records as noted in Note 2 in accordance
with the accounting principles and practices prescribed by the Japanese Ministry of Finance (the “MOF”),
which vary in some respects from U.S. GAAP. Those differences are mainly: that insurance acquisition costs
are deferred and amortized generally over the premium-paying period of the insurance policies, that future
policy benefits calculated locally under the authorization of the MOF are comprehensively adjusted to a net
level premium method with certain adjustments of actuarial assumptions and that deferred income taxes are
not recognized under local accounting practices. For purposes of preparing the consolidated financial state-
ments, appropriate adjustments have been made to reflect such items in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
The amounts of statutory net equity as of March 31, 1996 and 1997 were ¥12,624 million and ¥12,625
million ($101,815 thousand), respectively.
Deferred insurance acquisition costs
Insurance acquisition costs to be deferred, such as commission expenses, medical examination and inspection
report fees, etc., vary with and are primarily related to acquiring new insurance policies and are amortized
mainly over the premium-paying period of the related insurance policies using assumptions consistent with those
used in computing policy reserves. Amortization charged to income for the years ended March 31, 1995, 1996
and 1997 amounted to ¥7,148 million, ¥9,694 million and ¥15,855 million ($127,863 thousand), respectively.
Future insurance policy benefits
Liabilities for future policy benefits are established in amounts adequate to meet the estimated future
obligations of policies in force. These liabilities are computed by the net level premium method based upon
estimates as to future investment yield, mortality and withdrawals. Future policy benefits are computed using
interest rates ranging from approximately 3.5% to 6.25%, generally graded down after 10 to 20 years.
Mortality, morbidity and withdrawal assumptions for all policies are based on either the life insurance
subsidiary’s own experience or various actuarial tables. At March 31, 1996 and 1997, future insurance policy
benefits amounted to ¥392,119 million and ¥528,204 million ($4,259,710 thousand), respectively.
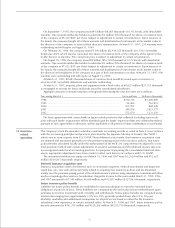
11. Insurance-
related
operations
On September 1, 1995, the company issued ¥1 billion ($8,065 thousand) of 0.1% bonds, with detachable
warrants. One warrant entitles the holders to subscribe ¥2 million ($16 thousand) for shares of common stock
of the company at ¥5,330 ($43) per share (subject to adjustment in certain circumstances). Upon issuance of
the bonds, the company bought all of these warrants and distributed such instruments at fair market value to
the directors of the company as a part of their directors’ remuneration. At March 31, 1997, 255 warrants were
outstanding and will expire on August 31, 1999.
On February 26, 1996, the company issued ¥ 300 billion ($2,419,355 thousand) of 0.15% convertible
bonds due 2001, which may be converted into shares of common stock of the company, at the option of the
holder thereof, at any time. The conversion price is subject to adjustment in certain circumstances.
On August 16, 1996, the company issued ¥2 billion ($16,129 thousand) of 0.1% bonds, with detachable
warrants. One warrant entitles the holders to subscribe ¥2 million ($16 thousand) for shares of common stock
of the company at ¥7,022 ($57) per share (subject to adjustment in certain circumstances). Upon issuance of
the bonds, the company bought all of these warrants and distributed such instruments at fair market value to
the directors and employees of the company as a part of their remuneration or salary. At March 31, 1997, 909
warrants were outstanding and will expire on August 15, 2000.
At March 31, 1997, 80,083 thousand shares of common stock would be issued upon conversion or
exercise of all convertible debentures and warrants outstanding.
At March 31, 1997, property, plant and equipment with a book value of ¥4,627 million ($37,315 thousand)
is mortgaged as security for loans and bonds issued by consolidated subsidiaries.
Aggregate amounts of annual maturities of long-term debt during the next five years are as follows:
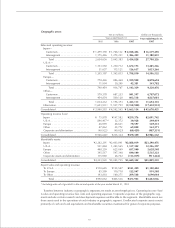
Year ending March 31 Yen in millions Dollars in thousands
1998 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ¥210,315 $1,696,089
1999 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94,465 761,815
2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107,705 868,589
2001 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348,834 2,813,177
2002 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152,670 1,231,210
The basic agreements with certain banks in Japan include provisions that collateral (including sums on de-
posit with such banks) or guarantors will be furnished upon the banks’ request and that any collateral furnished,
pursuant to such agreements or otherwise, will be applicable to all present or future indebtedness to such banks.