Sony 1997 Annual Report Download - page 54
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 54 of the 1997 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
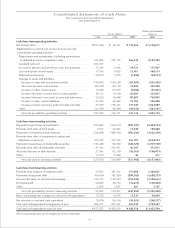
52
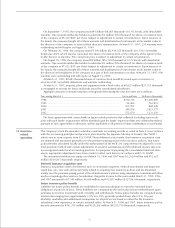
The company has certain financial instruments including financial assets and liabilities and off-balance-sheet
financial instruments incurred in the normal course of business. In applying a consistent risk management
strategy, the company manages its exposure to market rate movements of its financial assets and liabilities
through the use of derivative financial instruments which include currency forward exchange and option
contracts and interest rate currency swap agreements designated as hedges. These instruments are executed
with creditworthy financial institutions, and virtually all foreign currency contracts are denominated in U.S.
dollars, German mark and other currencies of major industrialized countries. Although the company may be
exposed to losses in the event of nonperformance by counterparties or interest and currency rate movements,
it does not anticipate significant losses due to the nature of its counterparties or the hedging arrangements.
Following are explanatory notes regarding the financial assets and liabilities and off-balance-sheet finan-
cial instruments.
Cash and cash equivalents, time deposits and notes and accounts receivable, trade
In the normal course of business, substantially all cash and cash equivalents, time deposits and notes and
accounts receivable, trade, are highly liquid and are carried at amounts which approximate fair value.
Notes and accounts payable, trade
In the normal course of business, substantially all notes and accounts payable, trade, are to be paid currently
and their carrying amounts approximate fair value.
Short-term borrowings and long-term debt
The fair values of short-term borrowings and total long-term debt including the current portion were
estimated based on the discounted amounts of future cash flows using the company’s current incremental
borrowing rates for similar liabilities.
Derivative financial instruments
The company enters into various currency forward exchange contracts, interest rate swap and interest rate
currency swap agreements and foreign currency purchased and written options as a normal part of its risk
management efforts, which include those transactions designed as hedges but that do not qualify for hedge
accounting under U.S. GAAP. Gains and losses on those derivative financial instruments qualified for hedge
accounting are deferred and effectively offset gains and losses on the underlying hedged assets and liabilities
by recognizing them in the same period. Others used for hedging purposes but not qualified for hedge
accounting under U.S. GAAP are marked to market. Such off-balance-sheet activities comprise the following:
Foreign exchange forward contracts, the majority of which mature within three months, are used to hedge
the risk of changes in foreign currency exchange rates substantially associated with accounts receivable and
payable and commitments on future trade transactions denominated in foreign currencies.
The purpose of the company’s foreign currency hedging activities is to protect the company from the risk
that the eventual Yen net cash inflows resulting from the sale of products to foreign customers will be adversely
affected by changes in exchange rates. The contracted amounts outstanding at March 31, 1996 and 1997
were ¥843,090 million and ¥756,294 million ($6,099,145 thousand), respectively. The fair values of these
contracts were estimated based on the market quotes.
Interest rate swap and interest rate currency swap agreements mature during 1997 to 2006 and the related
differentials to be paid or received are recognized in interest expense over the terms of the agreements.
Currency swap portions of the interest rate currency swap agreements are marked to market at the end of
each period and the foreign exchange gain or loss recognized on the swap offsets the foreign exchange gain
or loss recorded on the foreign-denominated debt. These agreements were arranged to lower funding costs, to
diversify sources of funding and to limit the company’s exposure to loss in relation to underlying debt instru-
ments resulting from adverse fluctuations in foreign currency exchange and interest rates. At March 31, 1996
and 1997, the aggregate notional principal amounts of the interest rate swap agreements were ¥155,306
million and ¥176,705 million ($1,425,040 thousand), respectively, and those of the interest rate currency
swap agreements were ¥233,685 million and ¥300,269 million ($2,421,524 thousand), respectively. The fair
values of such agreements were estimated based on the discounted amounts of net future cash flows.
The company entered into foreign currency option purchased contracts in the notional amounts of
¥106,549 million and ¥196,990 million ($1,588,629 thousand) at March 31, 1996 and 1997, respectively.
These contracts, the majority of which expire within three months of the balance sheet dates, are used in
conjunction with the forward exchange contracts to hedge foreign currency exposure arising from accounts
receivable and commitments on future trade transactions denominated in foreign currencies. The company
also entered into foreign currency option written contracts in the notional amounts of ¥164,439 million and
12. Financial
instruments