Sony 2004 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2004 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.66
“Other” sales increased by 67.4 billion yen,
or 13.7 percent, to 557.7 billion yen. The in-
crease resulted from a significant increase in
sales to Sony Ericsson of mobile phone hand-
sets, reflecting an increase in the sales of Sony
Ericsson’s handsets. On the other hand, sales
of Aiwa products decreased in all regions.
In the Electronics segment, cost of sales for
the fiscal year ended March 31, 2004 de-
creased by 34.6 billion yen, or 0.9 percent to
3,834.6 billion yen compared with the previous
fiscal year. The cost of sales to sales ratio
remained unchanged year on year at 78.8
percent. Products that contributed to an im-
provement in the cost of sales to sales ratio
were PCs, which benefited from an emphasis
on profitability and an increase in the propor-
tion of high value added models in the product
line-up, and low temperature polisilicon LCDs,
which benefited from a significant expansion
in sales. Offsetting this improvement, however,
was a significant increase in the sales of mobile
phone handsets, produced for Sony Ericsson,
which have a relatively high cost of sales to
sales ratio. Restructuring charges recorded in
cost of sales amounted to 10.1 billion yen
compared with 22.2 billion yen in the previous
year. Research and development costs in-
creased 49.1 billion yen, or 12.9 percent, from
380.3 billion yen in the previous year to 429.4
billion yen.
Selling, general and administrative expenses
increased by 67.9 billion yen, or 6.8 percent to
1,068.7 billion yen compared with the previous
fiscal year. The primary reason for this increase
was an increase in restructuring charges. Of
the restructuring charges recorded in the
Electronics segment, the amount recorded in
selling, general and administrative expenses
increased by 86.2 billion yen from 36.4 billion
yen in the previous year to 122.6 billion yen.
Of the restructuring charges recorded in sell-
ing, general and administrative expenses, the
amount recorded for headcount reductions,
including reductions through the early retire-
ment program, was 117.1 billion yen, an in-
crease of 89.3 billion yen compared with the
previous fiscal year. In addition to these per-
sonnel related costs, restructuring charges were
recorded in relation to TV display CRT manu-
facturing facilities in Japan. In contrast to the
increase in restructuring charges, royalty ex-
penses decreased 20.4 billion yen and after
sales service expenses decreased 8.6 billion yen
compared with the previous fiscal year. The ra-
tio of selling, general and administrative ex-
penses to sales increased 1.5 percentage
points from 20.3 percent recorded in the previ-
ous fiscal year to 21.8 percent, due to the de-
crease in sales.
Loss on sale, disposal or impairment of
assets, net increased 0.3 billion yen to 29.4
billion yen compared with the previous fiscal
year. This amount includes 10.6 billion yen in
restructuring charges, which includes 5.2 billion
yen related to the TV display CRT manufacturing
facilities in Japan. The amount of restructuring
charges included in loss on sale, disposal or
impairment, net in the previous fiscal year was
13.9 billion yen.
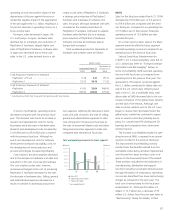
Regarding profit performance of the seg-
ment, an operating loss was recorded for the
fiscal year due to a significant increase in re-
structuring charges, especially severance-related
expenses, as mentioned above. Regarding profit
performance by product, excluding restructuring
charges, compared with the previous fiscal year,
operating income was recorded in PCs com-
pared with an operating loss in the previous
fiscal year, and a significant increase in operat-
ing income of CCDs was recorded. Losses from
Aiwa products decreased while the operating
income of CD-R/RW and DVD+/-R/RW drives,
as well as of video cameras, increased.
On the other hand, operating income of
CRT televisions decreased significantly while
operating income of optical pickups decreased
due to a sharp decline in prices. Furthermore,
personal digital assistants recorded an operat-
ing loss compared with operating income
recorded in the previous year.
Manufacturing by Geographic Area
Approximately 50 percent of the Electronics
segment’s total annual production took place
in Japan, including the production of digital
still cameras, video cameras, flat panel televi-
sions, PCs, semiconductors and components
such as batteries and Memory Sticks. Approxi-
mately 60 percent of the annual production in
Japan was destined for other regions. China
accounted for approximately 10 percent of
total annual production, approximately 60
percent of which was destined for Japan, the
U.S. and Europe. Asia, excluding Japan and
China, accounted for approximately 15 percent
of total annual production, with approximately
60 percent destined for Japan, the U.S. and
Europe. The Americas and Europe together
accounted for the remaining approximately 25
percent of total annual production, most of
which was destined for local distribution and
sale. Until July 2003, total annual production
included the assembly of PlayStation 2 hard-
ware for the Game segment; however, due to
the outsourcing of PlayStation 2 hardware
production to China-based third parties, this
assembly activity ceased in July 2003.
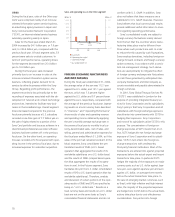
Comparison of Results on a Local Currency
Basis and Results on a Yen Basis
In the Electronics segment, the negative effect
of the appreciation of the yen against the U.S.
dollar slightly exceeded the positive effect of
the appreciation of the euro against the yen.
Sales for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2004
decreased, on a yen basis, by 0.9 percent, but
increased on a local currency basis by approxi-
mately 1 percent. In terms of operating perfor-
mance on a local currency basis, an operating
loss was recorded compared to operating
profit in the previous year, but the amount of
that loss was less than on a yen basis.
Regarding sales to outside customers by
geographic area, sales on a yen basis increased
in Japan by 11 percent, in Europe by 10 per-
cent, and in Other Areas by 8 percent. Sales on
a yen basis in the U.S decreased 7 percent.
Sales on a local currency basis increased in
every region, with sales in Japan increasing 11
percent, sales in Europe increasing 4 percent,
sales in Other Areas increasing 14 percent and
sales in the U.S. increasing 1 percent.
GAME
Sales for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2004
decreased by 174.8 billion yen, or 18.3 per-
cent, to 780.2 billion yen compared with the
previous fiscal year. Operating income de-
creased by 45.1 billion yen, or 40.0 percent, to
67.6 billion yen compared with the previous
fiscal year, and the operating income margin
decreased from 11.8 percent to 8.7 percent.
Sales in the Game segment on a local cur-
rency basis decreased 18 percent, approximately
the same as on a yen basis. In regards to