Siemens 2014 Annual Report Download - page 300
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 300 of the 2014 Siemens annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
108 A. To our Shareholders 131 B. Corporate Governance 171 C. Combined Management Report
NOTE Derivative financial instruments
and hedging activities
As part of the Company’s risk management program, a variety
of derivative financial instruments is used to reduce risks
resulting primarily from fluctuations in foreign currency ex-
change rates, interest rates and commodity prices.
The fair values of each type of derivative financial instruments
recorded as financial assets or financial liabilities are as follows:
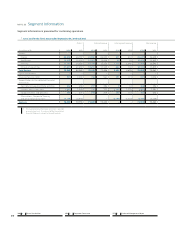
September , September ,
(in millions of €) Asset Liability Asset Liability
Foreign currency exchange
contracts 352 901 416 331
Interest rate swaps and
combined interest / currency
swaps 1,769 456 1,637 261
Commodity swaps 43 46 35 49
Embedded derivatives 212 30 118 122
Options 192 316 123 281
Credit Default Swaps – – – 4
2,569 1,749 2,330 1,047
FOREIGN CURRENCY EXCHANGE RATE
RISK MANAGEMENT
Derivative financial instruments
not designated in a hedging relationship
The Company manages its risks associated with fluctuations in
foreign currency denominated receivables, payables, debt, firm
commitments and forecast transactions primarily through
a Company-wide portfolio approach. Under this approach the
Company-wide risks are aggregated centrally, and various
derivative financial instruments, primarily foreign currency
exchange contracts, foreign currency swaps and options, are
utilized to minimize such risks. Such a strategy does not qualify
for hedge accounting treatment. Accordingly, all such deriva-
tive financial instruments are recorded at fair value on the Con-
solidated Statements of Financial Position, either in line items
Other current financial assets (liabilities) or line items Other
financial assets (liabilities); changes in fair values are charged
to net income (loss).
The Company also has foreign currency derivatives, which are
embedded in sale and purchase contracts denominated in a
currency that is neither the functional currency of the substan-
tial parties to the contract nor a currency which is commonly
used in the economic environment in which the contract
takes place. Gains (losses) relating to such embedded foreign
currency derivatives are reported in line item Cost of sales in
the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Hedging activities
The Company’s operating units apply hedge accounting for cer-
tain significant forecast transactions and firm commitments
denominated in foreign currencies. Particularly, the Company
has entered into foreign currency exchange contracts to reduce
the risk of variability of future cash flows resulting from fore-
cast sales and purchases as well as firm commitments. This risk
results mainly from contracts denominated in US$ both from
Siemens’ operating units entering into long-term contracts,
e.g. project business, and from the standard product business.
Cash flow hedges – As of September , and , the
ineffective portion of cash flow hedges is not significant indi-
vidually or in aggregate.
Periods in which the hedged forecast transactions or the firm
commitments denominated in foreign currency are expected to
impact profit or loss:
Year ended September ,
to
and
thereafter
(in millions of €)
Expected gain (loss)
to be reclassified from line item
Other comprehensive income,
net of income taxes into revenue
or cost of sales (166) (62) (94) 6
INTEREST RATE RISK MANAGEMENT
Interest rate risk arises from the sensitivity of financial assets
and liabilities to changes in market interest rates. The Company
seeks to mitigate that risk by entering into interest rate deriva-
tives such as interest rate swaps, options, interest rate futures
and forward rate agreements.
Derivative financial instruments
not designated in a hedging relationship
For the interest rate risk management relating to the Group
excluding SFS’ business, derivative financial instruments are
used under a portfolio-based approach to manage interest risk
actively relative to a benchmark. The interest rate management
relating to the SFS business remains to be managed separately,
considering the term structure of SFS’ financial assets and lia-
bilities on a portfolio basis. Neither approach qualifies for
hedge accounting treatment. Accordingly, all interest rate de-
rivatives held in this relation are recorded at fair value, either in
line items Other current financial assets (liabilities) or in line
items Other financial assets (liabilities), and changes in the fair
values are charged to line item Other financial income (ex-
penses), net. Net cash receipts and payments relating to inter-
est rate swaps used in offsetting relationships are also recorded
in line item Other financial income (expenses), net.