Toyota 2005 Annual Report Download - page 21
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 21 of the 2005 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Significant Differences in Corporate Governance Practices between Toyota and
U.S. Companies Listed on the NYSE
Pursuant to home country practices exemptions granted by the New York Stock Exchange (the
“NYSE”), Toyota Motor Corporation (the “Company”) is permitted to follow certain corporate
governance practices complying with Japanese laws, regulations and stock exchange rules in lieu of
NYSE’s listing standards. The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”)
approved changes to the NYSE’s listing standards related to corporate governance practices of listed
companies (the “NYSE Corporate Governance Rules”) in November 2003, as further amended in
November 2004. The Company is exempted from the approved changes, except for requirements
that (a) the Company’s board of corporate auditors satisfies the requirements of Rule 10A-3 under
the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), (b) the Company must
disclose significant differences in the corporate governance practices followed by the Company as
compared to those followed by domestic companies under the NYSE listing standards, (c) the
Company’s principal executive officer must notify the NYSE of material non-compliance with (a)
and (b), and (d) the Company must submit annual and interim written affirmations to the NYSE.
The Company’s corporate governance practices and those followed by domestic companies under
the NYSE Corporate Governance Rules have the following significant differences:
➤1. Directors The Company currently does not have any directors who will be deemed as an
“independent director” as required under the NYSE Corporate Governance Rules for U.S.
listed companies. Unlike the NYSE Corporate Governance Rules, the Commercial Code of
Japan (the “Code”) and the Law concerning Exceptional Measures to the Commercial Code
with respect to Auditing, etc. of Joint Stock Corporations (the “Special Exception Law”) do
not require Japanese companies with a board of corporate auditors such as the Company to
have any independent directors on its board of directors. While the NYSE Corporate
Governance Rules require that the non-management directors of each listed company meet
at regularly scheduled executive sessions without management, the Company currently has
no non-management director on its board of directors. Unlike the NYSE Corporate
Governance Rules, the Code and the Special Exception Law do not require, and accordingly
the Company does not have, an internal corporate organ or committee comprised solely of
independent directors.
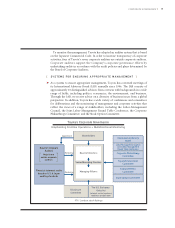
➤2. Committees Under the Code and the Special Exception Law, the Company has elected to
structure its corporate governance system as a company with corporate auditors, who are
under a statutory duty to monitor, review and report on the management of the affairs of the
Company. The Company, as with other Japanese companies with a board of corporate
auditors, but unlike U.S. listed companies subject to the NYSE Corporate Governance Rules,
does not have specified committees, including those that are responsible for director
nomination, corporate governance and executive compensation.
Pursuant to the Code, the Company’s board of directors nominates and submits a
proposal for the appointment of directors for shareholder approval. The shareholders vote on
such nomination at the Company’s general meeting of shareholders. The Code requires that
the respective total amount of remuneration to be paid to all directors and all corporate
auditors must be determined by a resolution of the general meeting of shareholders, unless
their remuneration is provided for in the Articles of Incorporation. The distribution of
remuneration among each director is broadly delegated to the Company’s board of directors
and the distribution of remuneration among each corporate auditor is determined by
consultation among the Company’s corporate auditors.
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE >19