Toyota 2005 Annual Report Download - page 22
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 22 of the 2005 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
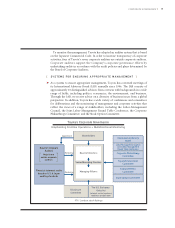
➤3. Audit Committee The Company avails itself of paragraph (c)(3) of Rule 10A-3 of the
Exchange Act, which provides a general exemption from the audit committee requirements
to a foreign private issuer with a board of corporate auditors, subject to certain requirements
which continue to be applicable under Rule 10A-3.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Code and the Special Exception Law, the Company
elects its corporate auditors through a resolution adopted at a general meeting of shareholders.
The Company currently has seven (7) corporate auditors, which exceeds the minimum number
of corporate auditors required pursuant to the Code and the Special Exception Law.
Unlike the NYSE Corporate Governance Rules, the Code and the Special Exception Law,
among others, do not require corporate auditors to establish an expertise in accounting nor
are they required to present other special knowledge and experience. Under the Special
Exception Law, the board of corporate auditors may determine the auditing policies and
methods of investigating the conditions of the business and the assets of the Company, and
may resolve other matters concerning the execution of the corporate auditor’s duties. The
board of corporate auditors also prepares auditors’ reports and gives consent to proposals of
the nomination of corporate auditors and accounting auditors.
The Company currently has four (4) outside corporate auditors under the Special Exception
Law. Under the Special Exception Law, at least one of the corporate auditors of the Company
must be an “outside” corporate auditor, which is such person who was not a director, executive
officer, manager, or employee of the Company or its subsidiaries during the five-year period
prior to such corporate auditor’s election. Such qualifications for an “outside” corporate
auditor are different from the audit committee independence requirement under the NYSE
Corporate Governance Rules.
➤4. Corporate Governance Guidelines Unlike the NYSE Corporate Governance Rules, the
Company is not required to adopt or disclose corporate governance guidelines under
Japanese laws and regulations including the Code and the Securities and Exchange Law of
Japan, or stock exchange rules. However, the Company is required to disclose policies and
the present status of its corporate governance in its annual securities report and certain other
disclosure documents in accordance with the regulations under the Japanese Securities and
Exchange Law and stock exchange rules in respect of timely disclosure.
➤5. Code of Business Conduct and Ethics Unlike the NYSE Corporate Governance Rules,
under Japanese laws and regulations including the Code and the Securities and Exchange Law
of Japan, or stock exchange rules, the Company is not required to adopt a code of business
conduct and ethics for directors, officers and employees. Accordingly, the Company is not
required to adopt and disclose waivers of the code of business conduct and ethics for these
individuals. However, the Company maintains guidelines and internal regulations such as
“Guiding Principles at the Company” and “Code of Conduct for the Company Employees” and
has also established a code of ethics pursuant to Section 406 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which
has been disclosed under the annual report on Form 20-F for the year ended March 31, 2003.
➤6. Shareholder Approval of Equity Compensation Plans Unlike the NYSE Corporate
Governance Rules, under which material revisions to equity-compensation plans of listed
companies are subject to shareholder approval, pursuant to the Code, if the Company desires
to adopt an equity-compensation plan under which stock acquisition rights are granted on
specially favorable terms to the recipient (except where such rights are granted to all of its
shareholders on a pro-rata basis at the same time), then the Company must obtain approval
by super-majority (as defined in the Code) at the general meeting of shareholders. Such
approval is applicable only to stock acquisition rights to be granted within one year from the
date of the approval.
20 >CORPORATE GOVERNANCE