Toyota 2005 Annual Report Download - page 69
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 69 of the 2005 Toyota annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS >67
OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
Securitization Funding
Toyota uses its securitization program as part of its
funding for its financial services operations. Toyota
believes that the securitizations are an important element
of its financial services operations as it provides a cost-
effective funding source.
Securitization of receivables allows Toyota to access a
highly liquid and efficient capital market while providing
Toyota with an alternative source of funding and investor
diversification. See note 7 to the consolidated financial
statements with respect to the impact on the balance sheet,
income statement, and cash flows of these securitizations.
Toyota’s securitization program involves a two-step
transaction. Toyota sells discrete pools of retail finance
receivables to a wholly-owned, bankruptcy remote special
purpose entity (“SPE”), which in turn transfers the
receivables to a qualified special purpose entity (“QSPE”
or “securitization trust”) in exchange for the proceeds
from securities issued by the securitization trust. Once the
receivables are transferred to the QSPE, the receivables are
no longer assets of Toyota and, therefore, no longer
appear in Toyota’s consolidated balance sheet. These
securities are secured by collections on the sold receivables
and structured into senior and subordinated classes.
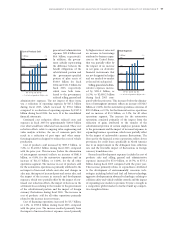
The following flow chart diagrams a typical securitiza-
tion transaction:
Toyota’s use of SPEs in securitizations is consistent with
conventional practices in the securitization markets. The
sale to the SPE isolates the sold receivables from other
creditors of Toyota for the benefit of securitization
investors and, assuming accounting requirements are
satisfied, the sold receivables are accounted for as a sale.
While Toyota retains subordinated interests, investors in
securitizations have no recourse to Toyota, any cash
reserve funds, or any amounts available or funded under
the revolving liquidity notes discussed below. Toyota does
not guarantee any securities issued by the securitization
trust. Each SPE has a limited purpose and may only be
used to purchase and sell the receivables. The individual
securitization trusts have a limited duration and generally
terminate when investors holding the asset-backed
securities have been paid all amounts owed to them.
The SPE retains an interest in the securitization trust.
The retained interest includes subordinated securities
issued by the securitization trust and interest-only strips
representing the right to receive any excess interest. The
retained interests are subordinated and serve as credit
enhancements for the more senior securities issued by the
securitization trust. The retained interests are held by the
SPE as restricted assets and are not available to satisfy any
obligations of Toyota. If forecasted future cash flows result
in an other-than-temporary decline in the fair value of the
retained interests, then an impairment loss is recognized
to the extent that the fair value is less than the carrying
amount. Such losses would be included in the consoli-
dated statement of income. These retained interests as well
as senior securities purchased by Toyota are reflected in
the consolidated balance sheet for accounting purposes.
Various other forms of credit enhancements are
provided to reduce the risk of loss for senior classes of
securities. These credit enhancements may include the
following:
Cash reserve funds or restricted cash
A portion of the proceeds from the sale of asset-backed
securities may be held by the securitization trust in
segregated reserve funds and may be used to pay principal
and interest to investors if collections on the sold
receivables are insufficient. In the event a trust experiences
charge-offs or delinquencies above specified levels,
additional excess amounts from collections on receivables
held by the securitization trusts will be added to such
reserve funds.
Off-balance
sheet
transaction
Toyota SPE
(Wholly-owned
by Toyota)
Investors
QSPE
(Securitization
Trust)
Receivables Receivables Securities
Proceeds
Proceeds Proceeds
Bankruptcy
remote
transaction