Sony 2000 Annual Report Download - page 81
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 81 of the 2000 Sony annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SONY CORPORATION ANNUAL REPORT 2000
79
12. Insurance-related operations
Sony’s stock life and non-life insurance subsidiaries in
Japan maintain accounting records as described in Note 2
in accordance with the accounting principles and prac-
tices prescribed by the Japanese Ministry of Finance (the
“MOF”), which vary in some respects from U.S. GAAP.
Those differences are mainly that insurance acquisi-
tion costs are charged to income when incurred in Japan
whereas in the United States of America those costs are
deferred and amortized generally over the premium-
paying period of the insurance policies, and that future
policy benefits calculated locally under the authoriza-
tion of the MOF are comprehensively adjusted to a net
level premium method with certain adjustments of actu-
arial assumptions for U.S. GAAP purposes. For purposes
of preparing the consolidated financial statements,
appropriate adjustments have been made to reflect
such items in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
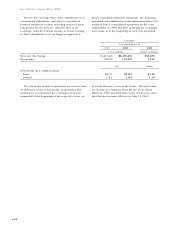
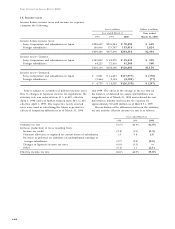
The amounts of statutory net equity of the subsidiar-
ies as of March 31, 1999 and 2000 were ¥40,626 million
and ¥49,791 million ($470 million), respectively.
Deferred insurance acquisition costs
Insurance acquisition costs, such as commission ex-
penses, medical examination and inspection report fees,
advertising costs, etc., that vary with and are primarily
related to acquiring new insurance policies are deferred
as long as they are recoverable. The deferred insurance
acquisition costs are amortized mainly over the pre-
mium-paying period of the related insurance policies
using assumptions consistent with those used in com-
puting policy reserves. Amortization charged to income
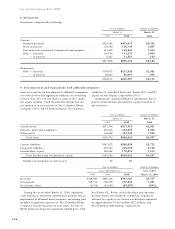
for the years ended March 31, 1998, 1999 and 2000
amounted to ¥21,838 million, ¥20,669 million and
¥22,708 million ($214 million), respectively.
Future insurance policy benefits
Liabilities for future policy benefits are established in
amounts adequate to meet the estimated future obliga-
tions of policies in force. These liabilities are computed
by the net level premium method based upon estimates
as to future investment yield, mortality and withdrawals.
Future policy benefits are computed using interest rates
ranging from approximately 2.25% to 5.5%, generally
graded down after 10 to 20 years. Mortality, morbidity
and withdrawal assumptions for all policies are based
on either the life insurance subsidiary’s own experience
or various actuarial tables.
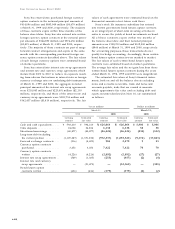
At March 31, 1999 and 2000, future insurance policy
benefits amounted to ¥865,814 million and ¥1,070,303
million ($10,097 million), respectively.
13. Financial instruments
Sony has certain financial instruments including finan-
cial assets and liabilities and off-balance-sheet financial
instruments incurred in the normal course of business.
In applying a consistent risk management strategy, Sony
manages the exposure to market rate movements of its
financial assets and liabilities through the use of derivative
financial instruments which include foreign exchange
forward contracts, foreign currency option contracts,
interest rate swap agreements and interest rate and
currency swap agreements designated as hedges. These
instruments are executed with creditworthy financial
institutions, and virtually all foreign currency contracts
are denominated in U.S. dollars, euros and other
currencies of major countries. Although Sony may be
exposed to losses in the event of nonperformance by
counterparties or interest and currency rate movements,
it does not anticipate significant losses due to the nature
of its counterparties or the hedging arrangements.
Following are explanatory notes regarding the
financial assets and liabilities and off-balance-sheet
financial instruments.
Cash and cash equivalents and time deposits
In the normal course of business, substantially all cash
and cash equivalents and time deposits are highly liquid
and are carried at amounts which approximate fair value.
Short-term borrowings and long-term debt
The fair values of short-term borrowings and total long-
term debt, including the current portion, were estimated
based on either the market value or the discounted
amounts of future cash flows using Sony’s current incre-
mental borrowing rates for similar liabilities.
Derivative financial instruments
Sony utilizes foreign exchange forward contracts and
foreign currency option contracts primarily to fix the
cash flow value resulting from accounts receivable and
payable and future transactions denominated in foreign
currencies in relation to the core currencies (Japanese
yen, U.S. dollars and euros) of Sony’s major operating
units.
Foreign exchange forward contracts, the majority of
which mature within three months, are used to hedge
this risk which is substantially associated with accounts
receivable and payable and anticipated transactions
denominated in foreign currencies. The contracted
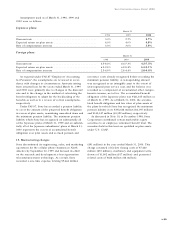
amounts outstanding at March 31, 1999 and 2000 were
¥718,474 million and ¥822,644 million ($7,761 million),
respectively. The fair values of these contracts were
estimated based on market quotations.