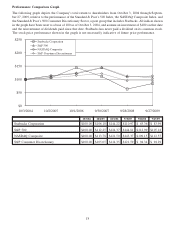
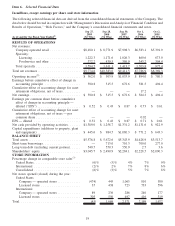
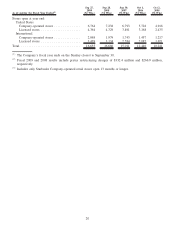
Starbucks 2009 Annual Report Download - page 20
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 20 of the 2009 Starbucks annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.receive considerable publicity or result in litigation, can significantly reduce brand value. Consumer demand for the
Company’s products and its brand equity could diminish significantly if Starbucks fails to preserve the quality of its
products, is perceived to act in an unethical or socially irresponsible manner or fails to deliver a consistently positive
consumer experience in each of its markets.
•The Company’s business depends in large part on the success of its business partners and suppliers, and
the Company’s brand and reputation may be harmed by actions taken by third parties that are outside of
the Company’s control.
The Company’s business strategy, including its plans for new stores, foodservice, branded products and other
initiatives, relies significantly on a variety of licensee and partnership relationships, particularly in its International
markets. Licensees are often authorized to use the Starbucks logo and provide Starbucks-branded beverages, food
and other products directly to customers. The Company provides training and support to, and monitors the
operations of, these business partners, but the product quality and service they deliver to Starbucks customers may
be diminished by any number of factors beyond the Company’s control, including financial pressures. Management
believes customers expect the same quality of products and service from the Company’s licensees as they do from
Starbucks and the Company strives to ensure customers have the same experience whether they visit a Company-
operated or licensed store. Any shortcoming of a Starbucks business partner, particularly an issue affecting the
quality of the service experience or the safety of beverages or food, may be attributed by customers to Starbucks,
thus damaging the Company’s reputation and brand value and potentially affecting the results of operations.
The Company’s products and in particular, its coffee and tea products, are sourced from a wide variety of domestic
and international vendors. The Company relies on international vendors to provide high quality product that comply
with applicable laws. The Company’s ability to find qualified vendors who meet our standards and supply products
in a timely and efficient manner is a significant challenge, especially with respect to goods sourced from outside the
US. These issues could negatively impact the Company’s business and profitability.
•The loss of key personnel or difficulties recruiting and retaining qualified personnel could jeopardize the
Company’s ability to meet its financial targets.
The Company’s success depends substantially on the contributions and abilities of key executives and other
employees, and on its ability to recruit and retain high quality employees to work in and manage Starbucks stores.
Starbucks must continue to recruit, retain and motivate management and other employees sufficient to maintain its
current business and support its projected growth. A loss of key employees or a significant shortage of high quality
store employees could jeopardize the Company’s ability to meet its financial targets.
•Effectively managing the Company’s growth is challenging.
Effectively managing growth can be challenging, particularly as Starbucks expands into new markets interna-
tionally, where it must balance the need for flexibility and a degree of autonomy for local management against the
need for consistency with the Company’s goals, philosophy and standards. Growth can make it increasingly difficult
to ensure a consistent supply of high quality raw materials, to locate and hire sufficient numbers of key employees to
meet the Company’s financial targets, to maintain an effective system of internal controls for a globally dispersed
enterprise and to train employees worldwide to deliver a consistently high quality product and customer experience.
•Adverse public or medical opinions about the health effects of consuming the Company’s products, as well
as reports of incidents involving food-borne illnesses or food tampering, whether or not accurate, could
harm its business.
Some Starbucks products contain caffeine, dairy products, sugar and other active compounds, the health effects of
which are the subject of increasing public scrutiny, including the suggestion that excessive consumption of caffeine,
dairy products, sugar and other active compounds can lead to a variety of adverse health effects. There has also been
greater public awareness that sedentary lifestyles, combined with excessive consumption of high-calorie foods,
have led to a rapidly rising rate of obesity. Particularly in the US, there is increasing consumer awareness of health
12